Search Engine Optimisation: A Comprehensive Guide
In the ever-evolving digital realm, one term stands as the linchpin between obscurity and online prominence: Search Engine Optimisation, or SEO. As the heartbeat of digital marketing, SEO is not just a buzzword; it’s the key to unlocking unparalleled visibility, driving organic traffic, and establishing a robust online presence.
Mastering the art and science of SEO is non-negotiable for businesses and individuals alike. Whether you’re a seasoned marketer looking to stay ahead of the curve or a newcomer aiming to demystify the complexities of online discoverability, this guide is your compass through the vast and dynamic terrain of SEO. From understanding the fundamentals of keyword research to navigating the intricacies of on-page and off-page optimisation, we unravel the nuances of SEO, providing you with insights that transcend algorithms and resonate with the core of user intent.
Here, we ensure that your online presence not only stands out but becomes an authoritative voice in your industry. Amplify your digital footprint and harness the true potential of SEO and unravel the secrets that will elevate your website from mere obscurity to the zenith of search engine rankings. Welcome to the comprehensive guide to SEO!
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to SEO
2. Search Engine Basics
3. Keyword Research
4. On-Page SEO
5. Off-Page SEO
6. Technical SEO
7. Local SEO
8. Mobile SEO
9. Youtube SEO
10. E-commerce SEO
11. SEO Analytics
12. SEO Reporting
13. Algorithm Updates and Trends
14. International SEO
15. SEO Best Practices
16. Artificial Intelligence in SEO

Introduction to SEO
Definition of SEO:
Search Engine Optimisation is the art and science of optimising online content to align with the criteria and algorithms of search engines, ultimately improving its visibility in search results. It involves a strategic approach to enhance a website’s relevance, credibility, and authority, making it more appealing to both search engines and users.
At the heart of SEO lies the understanding that search engines aim to deliver the most relevant and high-quality results to users’ queries. As such, SEO professionals work to align a website’s content, structure, and other elements with the preferences of search engine algorithms, ensuring that the website appears prominently when users search for relevant topics.
The Purpose of SEO:
Visibility and Ranking:
The primary purpose of SEO is to increase a website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). Higher visibility often translates to better rankings, making it more likely for users to click on the link.
Traffic Generation:
SEO is a potent tool for driving organic traffic to a website. By optimising for relevant keywords, a website is more likely to attract users genuinely interested in its content or products.
Credibility and Trust:
Websites that appear at the top of search results are often perceived as more credible and trustworthy by users. SEO efforts contribute to building this credibility through optimised content, user-friendly design, and authoritative backlinks.
User Experience Improvement:
SEO is not solely about appeasing search engine algorithms; it also focuses on enhancing the overall user experience. This includes factors like page speed, mobile responsiveness, and a well-structured website.
Competitive Edge:
In the crowded digital space, businesses and content creators vie for attention. SEO provides a competitive edge by ensuring that a website stands out in the vast sea of online content, making it more likely to attract and retain users.
Measurable Results:
One of the strengths of SEO is its measurability. Through analytics tools, SEO professionals can track the performance of their strategies, allowing for continuous refinement and improvement.
Adaptation to Evolving Trends:
Search engines are dynamic entities, frequently updating their algorithms to provide better results. SEO is a continuous process of adaptation, ensuring that a website remains relevant and visible amidst evolving search trends.
The definition and purpose of SEO encapsulate a dynamic and strategic approach to online visibility. By understanding and implementing SEO best practices, businesses and content creators can navigate the digital landscape with the goal of reaching and engaging their target audience effectively.
Importance of SEO in Online Marketing
Understanding the importance of SEO in online marketing is crucial for organisations seeking to thrive in the digital era.
1. Enhanced Visibility and Exposure:
At the heart of the importance of SEO lies its ability to amplify the visibility of a website or online content. In a world where search engines serve as the primary gateway to the internet, optimising content for search ensures that businesses are discoverable by a broader audience. Appearing on the first page of search engine results is akin to having a storefront on the busiest street in the digital marketplace.
2. Organic Traffic Acquisition:
SEO is a key driver of organic traffic, meaning the visitors who find a website through a search engine without the influence of paid advertising. Unlike paid methods, organic traffic is sustainable and often more cost-effective over the long term. By strategically optimising for relevant keywords, businesses can attract users actively seeking information, products, or services they offer.
3. Credibility and Trust Building:
Websites that consistently appear at the top of search results are perceived as more credible and trustworthy by users. SEO involves not only optimising for keywords but also creating high-quality content, improving user experience, and building authoritative backlinks. These elements collectively contribute to establishing a brand as an industry authority.
4. Improved User Experience:
SEO is not solely about pleasing search engines; it’s also about enhancing the overall user experience. Websites optimised for SEO often boast faster loading times, mobile responsiveness, and intuitive navigation. A positive user experience not only satisfies visitors but is also rewarded by search engines, contributing to better rankings.
5. Insightful Analytics and Measurement:
SEO allows for meticulous tracking and measurement of various metrics. Through tools like Google Analytics, businesses can gain insights into user behaviour, preferences, and the effectiveness of their SEO strategies. This data-driven approach empowers organisations to make informed decisions, refine their tactics, and adapt to the ever-changing digital landscape.
6. Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Paid Advertising:
While paid advertising can be effective, it comes with a price tag. SEO, on the other hand, offers a cost-effective alternative. While there are costs associated with SEO efforts, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment. Organic traffic, once established, continues to flow without the ongoing expenses of paid campaigns.
7. Adaptation to Mobile and Local Trends:
As mobile usage continues to surge, local searches have become integral to online marketing. SEO strategies are adaptable to mobile and local trends, ensuring that businesses can reach their audience regardless of the device or location. This adaptability is crucial in an era where consumers are constantly on the move.
In essence, the importance of SEO in online marketing cannot be overstated. It is a dynamic and multifaceted strategy that not only boosts visibility and traffic but also contributes to building credibility, improving user experience, and providing invaluable insights for continuous refinement. As businesses navigate the digital landscape, embracing and investing in SEO is not just a choice; it’s a fundamental necessity for sustained online success.
Evolution of Search Engines
The evolution of search engines stands as a testament to the rapid advancements in technology and the dynamic nature of the online landscape. From humble beginnings to the sophisticated algorithms of today, the journey of search engines has reshaped the way we access information, connect with the world, and conduct business. Let’s walk through the key milestones in the evolution of search engines.
1. The Dawn of Web Directories:
The concept of organising the web dates back to the early days of the internet. In the ’90s, web directories like Yahoo and Open Directory Project manually curated and categorised websites. Users navigated through hierarchical lists to find relevant information, but as the web expanded, this method proved inefficient and unsustainable.
2. Emergence of Keyword Indexing:
The late ’90s witnessed a pivotal shift with the advent of keyword indexing. Search engines like AltaVista and Lycos introduced algorithms that scanned web pages for keywords, revolutionising the way users discovered content. However, the sheer volume of web pages posed a challenge, leading to the need for more sophisticated algorithms.
3. Google’s PageRank Algorithm:
The turn of the millennium marked a seismic shift in the search engine landscape with the arrival of Google. Larry Page and Sergey Brin’s PageRank algorithm not only considered keywords but also assessed the importance of pages based on the quantity and quality of links. This innovation significantly improved search accuracy and relevance, propelling Google to the forefront of the search engine race.
4. Rise of User-Centric Search:
As the internet became woven into the fabric of daily life, search engines started incorporating user behaviour into their algorithms. Personalised search results, tailored to individual preferences and search history, became the norm. Google’s emphasis on delivering a personalised and localised experience further enhanced the user-centric approach to search.
5. Mobile-First Indexing:
The advent of smartphones prompted search engines to adapt to the mobile-centric habits of users. Mobile-first indexing became a priority, ensuring that websites optimised for mobile devices received favourable rankings. This evolution recognised the shift in user behaviour towards accessing information on the go.
6. Natural Language Processing and Voice Search:
Advancements in natural language processing and the rise of virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa ushered in the era of voice search. Search engines began interpreting conversational queries, understanding context, and delivering more nuanced results. This evolution reflected the growing reliance on voice-activated technology in our daily lives.
7. Machine Learning and AI Integration:
The contemporary landscape sees search engines employing machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to understand user intent better. Algorithms are now capable of analysing the semantics of content, recognising patterns, and providing more accurate and contextually relevant results. Google’s BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) update is a prime example of this AI-driven approach.
8. Video and Visual Search:
With the explosion of visual content, search engines have evolved to accommodate image and video searches. Google Lens, for instance, allows users to search using images captured by their cameras. This evolution caters to the growing preference for visual content consumption.
As we traverse the annals of search engine history, it’s evident that the evolution of these digital gatekeepers has been marked by innovation, adaptability, and a relentless pursuit of enhancing user experience. The journey is far from over, and with emerging technologies like augmented reality and further AI integration, the future promises even more intriguing chapters in the evolution of search engines.

Search Engine Basics
How Search Engines Work
The intricate workings of search engines serve as the silent architects of our online journeys. Understanding how search engines operate is akin to unlocking the door to the boundless repository of knowledge that the internet holds. Let’s unravel the mechanics of search engines and explore the journey from a user’s query to the delivery of relevant search results.
1. Web Crawling:
At the heart of search engine functionality lies the process of web crawling. Search engines deploy automated programs called crawlers or spiders to systematically navigate the web. These crawlers follow hyperlinks from one page to another, indexing the content they encounter. This vast collection of indexed pages forms the basis for what search engines can present to users in response to their queries.
2. Indexing:
Once the crawlers traverse the web and gather information, the next step is indexing. Indexing involves organising and storing the collected data in a structured manner. The search engine creates an index, which is essentially a massive database that allows for quick retrieval of relevant information when a user initiates a search. The index is finely tuned to ensure efficient and accurate search results.
3. Ranking Algorithms:
When a user enters a query into a search engine, the system activates complex algorithms to sift through the indexed data and determine the most relevant results. These algorithms take into account a myriad of factors, including keyword relevance, content quality, user experience, and the authority of the website. One of the seminal innovations in this realm was Google’s PageRank algorithm, which analysed the link structure of the web to assess the importance of pages.
4. Query Processing:
As a user submits a search query, the search engine processes the input to understand the user’s intent. Modern search engines employ natural language processing and semantic analysis to comprehend the nuances of human language, ensuring that the results are not just keyword-matched but contextually relevant.
5. Retrieval and Display:
Once the ranking algorithms have done their work, the search engine retrieves the most relevant results from its index. The results are then displayed to the user in the form of a Search Engine Results Page (SERP). The SERP typically includes a mix of organic results, paid advertisements, and additional features such as featured snippets, knowledge panels, and images.
6. Continuous Learning and Updates:
Search engines are not static entities; they evolve continuously. To keep up with the ever-changing landscape of the internet, search engines undergo regular updates and improvements. Algorithm updates, such as Google’s BERT update, introduce advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of search results.
7. User Feedback Loop:
Search engines also rely on user feedback to refine their algorithms. Click-through rates, time spent on pages, and other user engagement metrics provide valuable insights. This feedback loop allows search engines to adapt to changing user behaviour and preferences, ensuring that the results they deliver align with user expectations.
In essence, the operation of search engines is a symphony of intricate processes, algorithms, and continuous learning. From the initial crawl through the vast expanse of the web to the delivery of personalised and relevant search results, search engines play a pivotal role in shaping our digital experiences. Understanding this journey empowers users and content creators alike to navigate the digital landscape with a clearer perspective.
Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking
In the digital universe, where information sprawls across countless web pages, the seamless functioning of search engines relies on three fundamental processes: crawling, indexing, and ranking. These pillars form the backbone of search engine operations, working in concert to deliver relevant and meaningful results to users. Let’s delve into each of these processes to unravel the inner workings of search engines.
1. Crawling: The Digital Expedition
At the heart of search engine operations is the process of crawling, where automated bots, often referred to as crawlers or spiders, embark on a digital expedition across the vast landscape of the internet. These bots traverse web pages by following links, discovering and cataloguing content along the way. Imagine them as tireless explorers mapping out the expansive terrain of the World Wide Web.
Crawlers systematically visit web pages, collecting information and storing it for future analysis. This continuous exploration ensures that search engines have a comprehensive understanding of the content available on the internet. Notably, the frequency of crawling can vary based on factors such as the popularity and update frequency of a particular website.
2. Indexing: Organising the Digital Library
Once the crawlers return from their journey, the collected data undergoes a meticulous organisational process known as indexing. Think of indexing as creating a meticulously catalogued library where each book (web page) is assigned a specific location and category.
The search engine indexes the content, analysing keywords, metadata, and other relevant information. This organised index becomes the reference point for the search engine when responding to user queries. Efficient indexing is crucial for swift and accurate retrieval of information when users initiate a search.
3. Ranking: The Algorithmic Evaluation
When a user enters a query into a search engine, the real magic happens through the intricate dance of ranking algorithms. These algorithms, the secret sauce of search engines, evaluate a multitude of factors to determine the relevance and significance of each indexed page.
Ranking algorithms consider elements such as keyword relevance, content quality, user experience, and the authority of the website. The famed Google PageRank algorithm, for instance, revolutionised rankings by factoring in the importance of pages based on the quantity and quality of links.
The culmination of these evaluations results in the presentation of Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), showcasing the most relevant and valuable content based on the user’s query. The goal is to provide users with a seamless and efficient means of accessing the information they seek.
Search Engine Processes:
Crawling, indexing, and ranking operate in a symbiotic relationship, each process dependent on the other for optimal functionality. Crawling provides the raw data, indexing organises this data into a structured format, and ranking algorithms ensure that users receive the most pertinent results.
This trio of processes is not static; it’s a dynamic cycle that repeats constantly to keep search engines current and responsive to the ever-evolving digital landscape. As technology advances and user behaviours change, search engines continue to refine and enhance these processes, ensuring that users can navigate the vast expanse of the internet with ease and precision.
Major Search Engines – Google, Bing, and Yahoo
In the internet, search engines serve as the gatekeepers to information, guiding users through the vast expanse of digital content. While numerous search engines exist, three giants have emerged as the primary navigators of the digital domain: Google, Bing, and Yahoo. Each possesses its unique features, algorithms, and user experiences, contributing to the diverse landscape of online search.
Google: The Search Titan
Overview:
Google, founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, stands as the undisputed titan of the search engine realm. Its dominance is reflected in its overwhelming market share, with billions of searches conducted daily.
Key Features:
- PageRank Algorithm: Google’s innovative PageRank algorithm revolutionised search by considering the importance of pages based on the quantity and quality of links.
- Knowledge Graph: Google’s Knowledge Graph enhances search results by providing information directly in response to queries, offering a wealth of contextual knowledge.
- Rich Snippets: Google’s SERPs often feature rich snippets, providing users with more detailed information directly on the search results page.
User Experience:
- Google is renowned for its clean and minimalist design, emphasising speed and efficiency in delivering search results.
- Features like personalised search, voice search, and predictive typing enhance the overall user experience.
Bing: Microsoft’s Challenger
Overview:
Launched by Microsoft in 2009, Bing has positioned itself as a worthy challenger to Google’s supremacy. While it holds a smaller market share, Bing continues to attract users with its distinct features.
Key Features:
- Visual Search: Bing incorporates visual search, allowing users to search for information using images rather than text.
- Integration with Microsoft Services: Bing is tightly integrated with Microsoft’s suite of services, including Windows, Office, and Edge browser.
- Daily Background Images: Bing is known for its daily-changing background images, showcasing stunning visuals and providing interesting information.
User Experience:
- Bing focuses on delivering visually appealing search results, often presenting a different high-quality background image each day.
- Its video previews and image search features contribute to a multimedia-rich search experience.
Yahoo: A Pioneer Reinvented
Overview:
Yahoo, once a dominant player in the early days of the internet, has undergone transformations and strategic partnerships. In terms of search, it has been powered by Bing since 2009 through a partnership with Microsoft.
Key Features:
- Yahoo Directory: Yahoo’s directory, reminiscent of its early days, categorises websites for users to explore by topic.
- Integration with Yahoo Services: Yahoo’s search is closely integrated with its diverse range of services, including Yahoo Mail, Yahoo Finance, and more.
- News and Entertainment: Yahoo’s search results often include a blend of news and entertainment content.
User Experience:
- Yahoo maintains a user-friendly interface with a focus on delivering a broad array of content beyond traditional search results.
- Its integration with Yahoo’s ecosystem makes it a convenient choice for users engaged with other Yahoo services.
A Diverse Search Ecosystem
In the diverse landscape of major search engines, Google, Bing, and Yahoo each offer a unique entry point into the digital world. Google’s precision and innovation, Bing’s visual focus and integration, and Yahoo’s integration with a range of services collectively contribute to a rich and varied search ecosystem. Users can choose the search engine that aligns with their preferences, needs, and the overall digital experience they seek. As these platforms continue to evolve, the digital journey for users worldwide remains dynamic and full of exploration.

Keyword Research
Importance of Keywords in SEO
In Search Engine Optimisation (SEO), keywords emerge as the linchpin, serving as the vital link between users and the vast expanse of online content. Understanding the profound importance of keywords in SEO is paramount for businesses and content creators aiming to enhance their online visibility and connect with their target audience.
1. Defining the Essence: Keywords in SEO
At its core, a keyword is a term or phrase that encapsulates the essence of a piece of content. In the context of SEO, keywords are the words and phrases that users enter into search engines when seeking information, products, or services. The strategic integration of these keywords into web content facilitates the alignment between user intent and the content that a website provides.
2. Gateway to Discoverability:
Keywords serve as the gateway to enhanced discoverability on search engine results pages (SERPs). When a website is optimised for relevant keywords, it increases the likelihood of being prominently featured in search results when users initiate a search. Effective keyword optimisation acts as a beacon, guiding users to content that precisely addresses their queries.
3. Understanding User Intent:
In the dynamic landscape of SEO, keywords go beyond mere strings of text — they encapsulate user intent. By deciphering the language users employ in search queries, businesses gain valuable insights into the needs, preferences, and pain points of their target audience. This understanding forms the foundation for crafting content that not only incorporates keywords but resonates authentically with the users’ objectives.
4. Enhancing Content Relevance:
The incorporation of keywords into content enhances its relevance to both users and search engines. Well-researched and strategically placed keywords signal to search engine algorithms that a piece of content is pertinent to specific topics. This, in turn, contributes to higher rankings on SERPs, ensuring that the content reaches its intended audience.
5. Tailoring Content for SEO Success:
Keywords act as guideposts for content creation. By conducting thorough keyword research, businesses can identify the terms and phrases that are most relevant to their industry, products, or services. This research informs the creation of content that not only addresses user queries but aligns seamlessly with the language users naturally use during searches.
6. Diversifying Strategies with Long-Tail Keywords:
In addition to generic keywords, long-tail keywords play a pivotal role in SEO. These more specific, niche-focused phrases may have lower search volumes, but they often translate into higher conversion rates. Long-tail keywords allow businesses to refine their targeting, reaching users who are closer to making a decision or a purchase.
7. Adapting to Trends and Changes:
The landscape of online searches is dynamic, with user behaviour and trends continually evolving. Regular keyword analysis enables businesses to adapt their SEO strategies to align with shifting user preferences and emerging industry trends. Staying attuned to keyword dynamics ensures that content remains fresh, relevant, and in sync with the ever-changing digital environment.
A Strategic Imperative
In the symphony of SEO, keywords play a strategic and indispensable role. They are not merely strings of text but the keynotes that harmonise user intent with content relevance. Businesses and content creators who recognise and leverage the importance of keywords position themselves at the forefront of the digital stage, ensuring that their content resonates with audiences and ranks prominently in the dynamic realm of online searches.
Tools for Keyword Research in SEO
Successful navigation through the digital landscape begins with meticulous keyword research. This process involves not only identifying relevant terms but also understanding user intent and tailoring content to meet those needs. The journey of effective keyword research is made considerably more efficient and insightful with the aid of specialised tools. Here, we delve into some of the indispensable tools that have become the linchpin for businesses and content creators aiming to master the art of SEO.
1. Google Keyword Planner: The Nexus of Insight
Overview:
As a free and integral component of Google’s advertising platform, the Google Keyword Planner is a go-to resource for advertisers and SEO professionals alike. Designed to assist in building robust Google Ads campaigns, this tool offers valuable insights into search volumes, competition levels, and potential keywords.
Key Features:
- Keyword Suggestions: Google Keyword Planner generates a wealth of keyword suggestions based on user inputs, helping users discover new and relevant terms.
- Search Volume Trends: Users can explore historical search volume trends to understand the seasonality and popularity of keywords.
- Competition Analysis: The tool provides insights into the competitiveness of keywords, assisting in strategic decision-making.
2. SEMrush: The Swiss Army Knife of SEO
Overview:
SEMrush is an all-encompassing SEO toolkit that extends beyond keyword research to encompass various aspects of online visibility, competitor analysis, and content optimisation. Widely regarded as a comprehensive solution, SEMrush offers insights that go beyond basic keyword metrics.
Key Features:
- Keyword Analytics: SEMrush provides in-depth data on keyword metrics, including search volume, CPC (Cost Per Click), and keyword difficulty.
- Competitor Analysis: Users can explore the keywords that competitors are ranking for and identify potential gaps in their own strategies.
- Position Tracking: The tool enables tracking keyword positions over time, offering valuable insights into the success of SEO efforts.
3. Ahrefs: Unveiling Backlink Insights
Overview:
While Ahrefs is renowned for its prowess in backlink analysis, it also serves as a formidable tool for keyword research. Ahrefs provides a robust suite of features that empowers users to unravel the intricacies of their competitors’ strategies and optimise their own content accordingly.
Key Features:
- Keyword Explorer: Ahrefs’ Keyword Explorer offers insights into search volume, clicks data, and keyword difficulty, aiding in the selection of high-impact keywords.
- Content Gap Analysis: Users can identify keywords for which competitors rank but their own site does not, facilitating the discovery of new opportunities.
- SERP Analysis: Ahrefs provides a detailed analysis of search engine results pages (SERPs) for specific keywords, helping users understand the competitive landscape.
4. Ubersuggest: From Suggestion to Strategy
Overview:
Ubersuggest, founded by Neil Patel, has gained popularity as a user-friendly and accessible keyword research tool. Designed with simplicity in mind, Ubersuggest provides a plethora of insights to guide users in optimising their content for search engines.
Key Features:
- Keyword Suggestions: Ubersuggest generates extensive lists of keyword suggestions, making it a valuable resource for discovering new and niche terms.
- Competitor Analysis: Users can gain insights into the keywords for which competitors rank, helping refine their own keyword strategies.
- Content Ideas: Ubersuggest goes beyond keywords to offer content ideas based on popular topics and search trends.
Empowering SEO Excellence
The landscape of SEO is dynamic, and staying ahead requires precision, insight, and adaptability. Tools for keyword research are not mere utilities; they are the compasses that guide businesses and content creators toward digital success. Whether delving into Google Keyword Planner for foundational insights, harnessing the comprehensive capabilities of SEMrush, exploring the backlink-driven insights of Ahrefs, or embracing the user-friendly interface of Ubersuggest, these tools collectively empower SEO excellence, ensuring that every keyword selected aligns seamlessly with user intent and business objectives in the ever-evolving digital terrain.
Long-tail Keywords and their Significance
In Search Engine Optimisation (SEO), where the digital battleground is vast and competitive, the strategic use of keywords takes centre stage. Amidst the plethora of terms and phrases, long-tail keywords emerge as unsung heroes, wielding a unique power that goes beyond mere search queries. Understanding the significance of long-tail keywords is crucial for businesses and content creators aiming to refine their SEO strategies and connect with a more targeted audience.
1. Defining Long-Tail Keywords:
Long-tail keywords are specific and typically longer phrases that users enter into search engines when seeking highly targeted information or solutions. Unlike short and broad keywords, long-tail keywords are more detailed and specific, reflecting the nuanced queries users often pose. For example, while a broad keyword might be “running shoes,” a long-tail variant could be “best lightweight running shoes for flat feet.”
2. Precision in User Intent:
One of the key advantages of long-tail keywords lies in their ability to capture user intent with exceptional precision. Users employing long-tail queries often have a clear idea of what they are seeking, whether it’s specific product features, solutions to niche problems, or detailed information on a particular topic. Tailoring content to these specific queries allows businesses to align seamlessly with user expectations.
3. Lower Competition, Higher Conversion:
Long-tail keywords often exhibit lower search volumes compared to broad keywords. While this might seem like a disadvantage at first glance, it actually presents an opportunity. Long-tail keywords tend to have less competition, making it easier for businesses to rank higher for these terms. Additionally, users searching with long-tail queries are typically further along in the purchase funnel, resulting in higher conversion rates.
4. Enhanced Relevance and User Engagement:
Tailoring content around long-tail keywords enables businesses to create highly relevant and targeted material. When users find content that precisely addresses their specific queries, it fosters a sense of trust and authority. The result is increased user engagement, longer time spent on the page, and a higher likelihood of users taking desired actions, such as making a purchase or subscribing to a service.
5. Niche and Local Targeting:
Long-tail keywords are particularly valuable for businesses operating in specific niches or catering to local markets. These phrases allow for a more granular approach to SEO, helping businesses connect with audiences looking for specialised products, services, or information. For example, a local bakery might benefit from targeting a long-tail keyword like “best gluten-free bakery in [city].”
6. Adaptability to Voice Search:
As voice search continues to rise in popularity, the significance of long-tail keywords becomes even more pronounced. Users tend to articulate voice searches in a more conversational and natural manner, often resembling long-tail queries. Optimising content for these specific and detailed phrases positions businesses to capitalise on the growing trend of voice-activated searches.
7. Insights for Content Creation:
Long-tail keywords serve as a valuable source of insights for content creation. Analysing the specific terms users are searching for allows businesses to identify trends, pain points, and emerging topics within their niche. This, in turn, informs content strategies, ensuring that businesses are consistently delivering the information their audience is actively seeking.
Precision in a Crowded Landscape
In SEO, where every business vies for attention, the significance of long-tail keywords lies in their precision and ability to cut through the digital noise. These specific and targeted phrases not only enhance relevance and user engagement but also open doors to untapped opportunities in niche markets. As businesses refine their SEO strategies, embracing the unique power of long-tail keywords becomes a strategic imperative, offering a pathway to connect with a more qualified and motivated audience in the intricate dance of online discovery.

On-Page SEO
What is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO refers to the practice of optimising individual web pages to improve their ranking and visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). The goal of on-page SEO is to make web pages more relevant to search engine queries and improve their perceived value to users.
On-page SEO involves a variety of techniques, including optimising the content of the page (such as headlines, paragraphs, and images) for specific keywords, improving the page’s metadata (such as title tags and meta descriptions), optimising the page’s URL structure, and ensuring that the page is mobile-friendly and has fast load times.
In addition to improving the ranking of a web page in search engine results, on-page SEO can also improve user experience, making it easier for users to find and navigate relevant content on a website. On-page SEO, as previously mentioned, is the practice of optimising individual web pages in order to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. This involves a variety of different factors, including both the content and HTML source code of a page. These factors can include:
1. Keyword research and optimisation: Keyword research and optimisation are key components of search engine optimisation (SEO) that involve identifying relevant keywords or phrases that people use to search for information, products, or services online, and then strategically incorporating them into website content to improve search engine rankings and attract more targeted traffic.
Keyword research involves using various tools and techniques to identify relevant keywords or phrases that people are searching for related to a particular topic, product, or service. This can include analysing search volume, competition level, and user intent to determine which keywords are most likely to drive targeted traffic to a website.
Keyword optimisation, on the other hand, involves strategically incorporating these keywords into website content, including page titles, meta descriptions, headers, and body text, to improve search engine rankings and attract more targeted traffic. This requires careful consideration of keyword density, relevance, and placement, as well as other factors that can impact search engine visibility, such as page load speed and mobile-friendliness.
Overall, effective keyword research and optimisation are essential for improving search engine visibility, attracting targeted traffic, and ultimately driving conversions and sales for businesses operating online.
2. Title tags: Title tags, also known as title elements, are HTML elements that specify the title of a webpage. They appear in the head section of a webpage’s HTML code and are usually displayed in the browser’s title bar and in search engine results pages (SERPs).
The title tag is an important element for both users and search engines as it provides a concise and accurate description of the webpage’s content, helping users to understand what the page is about and search engines to determine its relevance to search queries. It is also one of the key factors that search engines use to determine the ranking of a webpage in search results.
It is important to make sure that the title tag is descriptive, relevant to the content of the page, and contains relevant keywords that users might use when searching for information related to the page’s content.
3. Meta descriptions: Meta descriptions are short HTML tags that provide a brief summary of the content of a web page. They typically appear underneath the title tag in search engine results pages (SERPs) and provide users with a preview of what they can expect to find on a particular page.
Meta descriptions are typically limited to around 155-160 characters in length and should accurately reflect the content of the page they describe. They also often contain relevant keywords that users might use to find the page, as search engines use these keywords to determine whether a particular page is relevant to a user’s search query.
While meta descriptions do not directly impact a page’s search engine ranking, they can play a critical role in driving traffic to a website by encouraging users to click through to the page from the search engine results page.
4. Headings: Headings are text elements that are used to organise and structure the content of a web page. Headings are typically larger and more prominent than regular body text and are used to indicate the hierarchy of information on a web page.
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), which is used to create web pages, provides six different levels of headings, from H1 (the most important) to H6 (the least important). The main heading of a web page is usually an H1, which provides a clear and concise summary of the page’s content.
Subheadings can be used to break the content into sections and subsections, with each level of heading indicating a different level of importance or priority. Proper use of headings can help make a web page more accessible and easier to navigate for both users and search engines.
5. Content optimisation: Content optimisation is the process of improving the quality and relevance of content on a website to increase its visibility and ranking on search engines like Google, Bing, etc. It involves optimising various elements of content such as title, headings, subheadings, meta descriptions, images, keywords, and overall structure to ensure that the content is easily understood by search engines and users.
The goal of content optimisation is to create content that provides value to the target audience while being easily discoverable by search engines. By optimising content, it becomes more likely to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs), leading to increased traffic, engagement, and conversions.
Content optimisation also involves improving user experience by ensuring that the content is easy to read, engaging, and relevant. This can include things like formatting, adding visuals, and making sure the content is up-to-date and accurate.
Overall, content optimisation is a critical aspect of any digital marketing strategy, as it can help improve a website’s visibility, attract more visitors, and ultimately drive more conversions.
6. Internal linking: Internal linking is the practice of linking one page of a website to another page within the same website. These links are typically used to help users navigate a site and find relevant content, as well as to help search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of a site.
Internal links can be created using text links, image links, or other types of clickable elements on a website. When a user clicks on an internal link, they are taken to another page within the same website.
Internal linking is an important aspect of website design and optimisation, as it can help improve the user experience and make it easier for search engines to crawl and index a site. By linking related pages together, website owners can also help boost the authority of individual pages and improve their search engine rankings.
Why is On-Page SEO Important?
On-page SEO is important because it plays a vital role in determining a website’s search engine ranking, which in turn can impact its visibility, traffic, and revenue.
Here are a few reasons why on-page SEO is important:
a. It can help to improve your search engine rankings: By optimising your web pages for relevant keywords and ensuring that your content is high-quality, you can increase your chances of ranking higher in search engine results pages.
b. It can help to attract more relevant traffic: By targeting the keywords and phrases that your target audience is searching for, you can attract more relevant traffic to your website. A higher ranking in search results means more visibility and click-throughs to your site.
c. It can help to improve the user experience: On-page SEO techniques such as optimising page load speed, using appropriate heading tags, adding relevant internal links and by ensuring that your content is high-quality and engaging, can improve the user experience on your website. This can lead to increased engagement, lower bounce rates, and higher conversions.
d. It can help to improve your website’s crawlability: By optimising your website’s HTML source code and internal linking structure, you can make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your pages.
Overall, on-page SEO is important because it helps your website rank higher in search results, improve user experience, increase organic traffic, and ultimately drive more conversions and revenue.
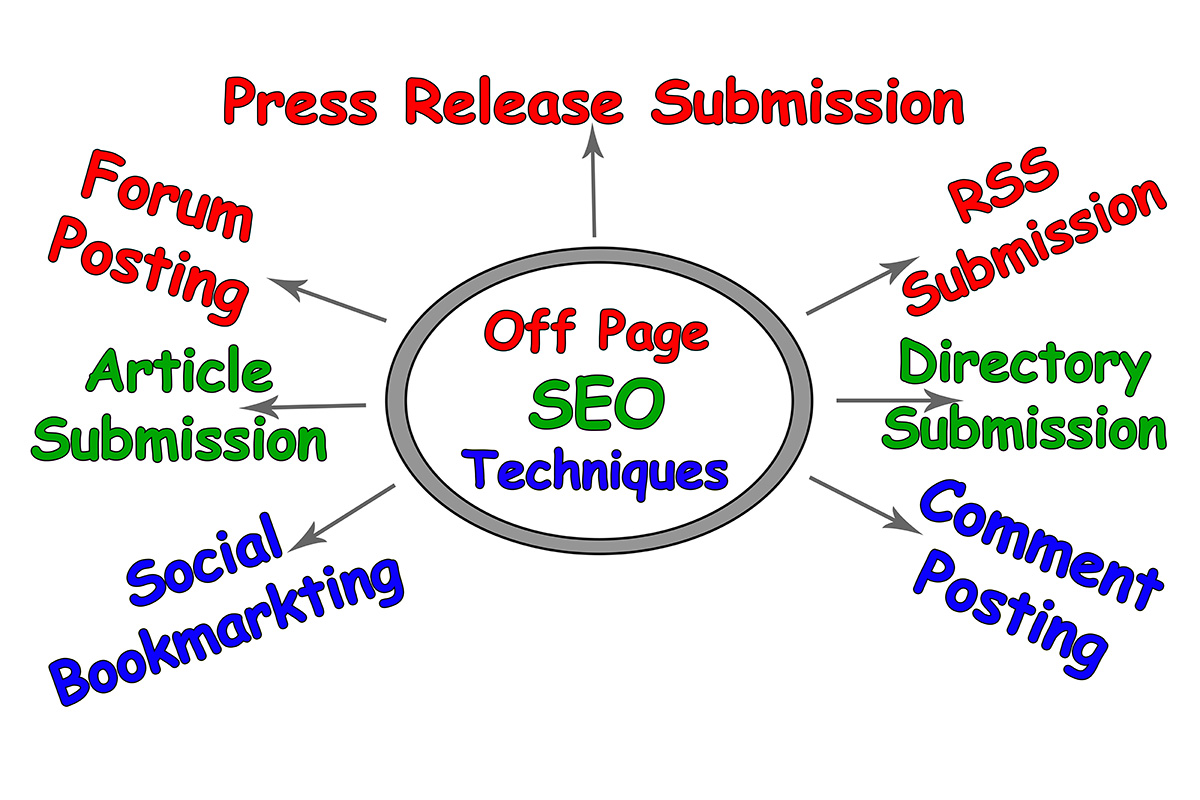
Off-Page SEO
What is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO refers to the activities that are done outside of a website to improve its search engine ranking. It involves optimising elements that are not directly controlled by the website owner, such as link building, social media promotion, and online reputation management.
The primary goal of off-page SEO is to increase the visibility and authority of a website in the eyes of search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. This can be achieved by acquiring high-quality backlinks from other reputable websites, sharing content on social media platforms, and engaging with the online community through forums, blogs, and other online communities.
Off-page SEO is an essential component of a comprehensive SEO strategy, as it helps to build a strong online presence and establish credibility with both search engines and users. However, it’s important to note that off-page SEO alone is not enough to achieve high search engine rankings, and it should be combined with on-page SEO and other digital marketing tactics for optimal results.
How to do Off-Page SEO Effectively
Here are some effective ways to do off-page SEO:
1. Build high-quality backlinks: Backlinks are a crucial ranking factor, and they are the most significant part of off-page SEO. However, not all backlinks are equal. Focus on building high-quality backlinks from authoritative websites in your niche.
Here are some strategies that you can use to build high-quality backlinks:
a. Create high-quality content: The best way to attract high-quality backlinks is to create high-quality content that people want to link to. This can include blog posts, infographics, videos, or other types of content that are informative, entertaining, or useful.
b. Guest posting: Guest posting is a great way to build high-quality backlinks. Find relevant websites in your niche that accept guest posts, and submit high-quality content with a link back to your website.
c. Broken link building: Broken link building involves finding broken links on other websites and reaching out to the website owner to suggest a replacement link, which could be to your own content. This can be a great way to build high-quality backlinks and also help the website owner by fixing their broken links.
d. Skyscraper technique: The Skyscraper technique involves finding popular content in your niche, creating even better content, and then reaching out to the people who linked to the original content to suggest that they link to your content instead.
e. Participate in online communities: Participating in online communities such as forums, social media groups, and Q&A sites can help you build relationships with other people in your niche, which can lead to opportunities for high-quality backlinks.
f. Infographics: Creating high-quality infographics is a great way to attract backlinks. Infographics are highly shareable and can be used as a visual aid in blog posts or other content.
Remember, when building backlinks, it’s important to focus on quality over quantity. Aim to build high-quality backlinks from authoritative websites in your niche, rather than spamming low-quality websites with links. Also, be sure to follow ethical and white-hat SEO practices to avoid penalties from search engines.
2. Social media marketing: Social media is a powerful tool to drive traffic to your website and build brand awareness. Share your content on relevant social media platforms to increase engagement and visibility. Additionally, social signals like likes, shares, and comments can indirectly impact your search engine rankings.
Here are some tips:
a. Build a Strong Social Media Presence: Create profiles on popular social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Pinterest. Make sure to complete your profile with all relevant information, including your website URL, and use consistent branding across all platforms.
b. Share Your Content on Social Media: Share your blog posts, articles, videos, and other content on social media to drive traffic back to your website. Be sure to use relevant hashtags and keywords in your social media posts.
c. Engage with Your Followers: Encourage your followers to engage with your content by asking questions, running polls, and responding to comments. Engaging with your followers can help you build a loyal following and improve your visibility on social media.
d. Leverage Influencer Marketing: Partner with influencers in your industry to promote your brand and products. Influencer marketing can help you reach new audiences and build backlinks to your website.
e. Monitor Your Social Media Metrics: Use analytics tools to monitor your social media metrics, such as engagement rates, follower growth, and website traffic. Analysing your social media metrics can help you refine your social media strategy and improve your off-page SEO.
3. Influencer marketing: When it comes to influencer marketing, the idea is to collaborate with influencers who have a large following and can help promote your brand or website to their audience. This can be done in several ways, such as sponsored posts, product reviews, and social media shoutouts.
By working with influencers, you can leverage their existing audience and reach a wider demographic that you may not have been able to reach otherwise. This can help increase your brand’s visibility and ultimately drive more traffic to your website.
In addition to driving traffic, influencer marketing can also help improve your website’s search engine rankings. This is because when an influencer shares a link to your website on their social media channels or website, it creates a backlink which is important for SEO because they signal to search engines that your website is a valuable resource and can help improve your search engine rankings.
Overall, influencer marketing is a powerful tool for off-page SEO and can help businesses of all sizes increase their online visibility and drive more traffic to their website.
4. Content marketing: Content marketing can be a highly effective off-page SEO strategy. By creating high-quality, relevant content that people want to read and share, you can build backlinks to your website, improve your online reputation, and increase your visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Tips for using content marketing for off-page SEO:
a. Create shareable content: Content that is informative, interesting, or entertaining is more likely to be shared on social media and other websites. Use your content to answer questions, provide valuable information, or tell stories that resonate with your target audience.
b. Guest blogging: Guest blogging on other relevant websites is a great way to build backlinks to your website. Reach out to websites that are relevant to your niche and offer to write a guest post for them. Make sure your content is high-quality, informative, and relevant to the audience of the website you are writing for.
c. Infographics: Infographics are a great way to present complex information in an easy-to-digest format. Create an infographic that provides valuable information related to your niche and promote it on social media and other websites. Make sure to include a link back to your website in the infographic.
d. Social media: Social media can be a powerful tool for promoting your content and building backlinks to your website. Share your content on social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn. Encourage your followers to share your content with their followers, which can help to build backlinks to your website.
e. Content syndication: Content syndication involves publishing your content on other websites with a link back to your website. Find relevant websites that are willing to publish your content and make sure to include a link back to your website in the article.
Remember, the key to successful off-page SEO through content marketing is to create high-quality content that is relevant, informative, and shareable. By doing so, you can build backlinks to your website, improve your online reputation, and increase your visibility in search engine results pages.
5. Brand building: Building a strong brand is an important aspect of off-page SEO as it can lead to increased visibility, authority, and trustworthiness, which in turn can improve your website’s rankings. This can be done through creating a unique brand voice, providing excellent customer service, and building relationships with your audience.
Tips for brand building for off-page SEO:
a. Build your brand’s online presence: This includes creating profiles on social media platforms, business directories, and review sites. Make sure your brand is listed accurately and consistently across all platforms.
b. Engage with your audience: Interact with your followers on social media, respond to customer reviews, and engage in conversations related to your brand. This will help build a loyal following and increase brand awareness.
c. Create shareable content: Develop content that is informative, entertaining, and shareable. This can include blog posts, infographics, videos, and more. Share your content on social media and other relevant platforms to increase its visibility and reach.
d. Focus on quality link building: Acquiring backlinks from high-quality, authoritative websites can improve your website’s rankings. Focus on building relationships with other brands and websites in your niche to earn valuable backlinks.
e. Monitor your online reputation: Regularly monitor your brand’s online reputation to address any negative reviews or comments. Responding in a timely and professional manner can help mitigate any damage to your brand’s reputation.
By focusing on brand building for off-page SEO, you can improve your website’s search engine rankings and increase your online visibility and authority.
Why is Off-Page SEO Important?
Off-page SEO is important for several reasons:
a. Boosts search engine rankings: Search engines consider off-page factors such as backlinks, social media signals, and online citations as indicators of a website’s popularity and authority. By building high-quality backlinks from authoritative websites, a website can improve its search engine rankings and visibility.
b. Increases website traffic: By ranking higher in search engine results, a website can attract more organic traffic to its pages. Additionally, off-page SEO efforts such as social media marketing and online advertising can drive more referral traffic to the website.
c. Enhances online reputation: Off-page SEO efforts such as managing online reviews and mentions can help businesses build a positive reputation and trust with their audience. A positive online reputation can lead to increased customer loyalty and sales.
d. Improves brand awareness: By building a strong online presence through off-page SEO efforts, a website can increase its brand visibility and awareness among its target audience.
In summary, off-page SEO is essential for improving a website’s search engine rankings, driving traffic, enhancing online reputation, and boosting brand awareness. Remember that off-page SEO is a long-term strategy, and it takes time and effort to see results. Focus on building relationships, creating value, and providing a great user experience, and you’ll see improvements in your search engine rankings over time.

Technical SEO
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimising a website’s technical aspects to improve its visibility and ranking on search engines and focuses on the backend of a website, such as the code and server-side configurations. This includes making sure that search engines can easily crawl and index your website, that your website is mobile-friendly and responsive, that your site speed is optimised, that your website has a proper URL structure, that your website has proper schema markup and other structured data, and that your website is secure and has proper SSL certification.
Technical SEO is a critical part of overall SEO strategy as it ensures that search engines can easily understand and rank your website. By optimising the technical aspects of your website, you can improve your search engine ranking and drive more organic traffic to your website. We will discuss technical SEO and how to improve it to increase your website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Why is Technical SEO important?
When a website is optimised for technical SEO, search engines can easily crawl and understand its content, resulting in higher rankings and more organic traffic. Technical SEO also helps in improving user experience and making the website more accessible to users with disabilities.
Without proper technical SEO, a website may not be able to rank well in search engine results pages (SERPs), which can lead to lower traffic, visibility, and revenue. Additionally, technical issues such as broken links, duplicate content, or slow page speed can negatively impact user experience and hurt a website’s credibility.
Overall, technical SEO is an important aspect of website optimisation that ensures that search engines and users can access, understand, and engage with a website effectively.
How to improve Technical SEO
1. Website Speed
Website speed is an essential aspect of technical SEO. A slow website can negatively impact your website’s user experience and search engine rankings. Improving website speed is crucial to ensure a smooth user experience and improve search engine rankings.
Here are some tips to help you improve your website speed:
a. Optimise images: Large images can slow down your website’s loading time. You can use image optimisation tools to compress and resize images without losing their quality.
b. Minimise HTTP requests: Reducing the number of HTTP requests can speed up your website. Combine multiple CSS and JavaScript files into a single file, and use CSS sprites to combine multiple images into a single image.
c. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN can help improve website speed by distributing your website’s content across multiple servers worldwide.
d. Enable caching: Caching allows your website to store static files, such as images and CSS, on the user’s device, which reduces the amount of data that needs to be loaded every time the user visits your site.
e. Minimise plugins: Plugins can be useful, but too many plugins can slow down your website. Only use the plugins that you need, and regularly update and delete any unnecessary ones.
f. Use a faster hosting provider: The speed of your website is also affected by the performance of your hosting provider. Choose a reliable hosting provider that has fast servers and good uptime.
g. Optimise code: Minimise the size of your code by removing unnecessary characters, spaces, and comments. Also, use a caching mechanism for dynamic pages and reduce the number of database queries.
By implementing these tips, you can improve your website speed and provide a better user experience for your visitors.
2. Mobile-friendliness
Mobile-friendliness is another critical aspect of technical SEO. With more than half of internet traffic coming from mobile devices, having a mobile-friendly website is crucial. To improve mobile-friendliness, you can implement the following strategies:
a. Choose a responsive design: A responsive design automatically adjusts the layout of your website to fit the screen size of the device being used. This ensures that your website looks good and is easy to navigate on any device.
b. Optimise images: Large images can slow down the loading time of your website on mobile devices. You can optimise images by compressing them without losing quality. This can improve loading times and make your website more mobile-friendly.
c. Simplify the navigation: Navigation menus can be difficult to use on smaller screens. Simplify your navigation by using a hamburger menu or reducing the number of menu items. This can make it easier for users to find what they are looking for on your website.
d. Use readable font sizes: Small font sizes can be difficult to read on mobile devices. Use a font size of at least 14px to ensure that your content is easy to read on smaller screens.
e. Use mobile-friendly forms: Mobile users may not want to fill out long forms on their devices. Use mobile-friendly forms that are easy to fill out and require minimal typing.
f. Test your website on different devices: Test your website on a variety of devices to ensure that it looks good and functions properly on all of them. You can use online tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check your website’s mobile-friendliness.
By following these steps, you can improve the mobile-friendliness of your website and provide a better user experience for mobile users.
3. Crawlability
Crawlability refers to how easily search engines can crawl and index your website. If search engines cannot crawl your website, it will not appear in SERPs. To improve crawlability, you can implement the following strategies:
a. Use a sitemap: A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website, and it helps search engines find all your content. Submit your sitemap to search engines to improve crawlability.
b. Fix broken links: Broken links can cause search engines to stop crawling your website. Use a broken link checker to find and fix any broken links on your website.
c. Improve website speed: A slow website can discourage search engine bots from crawling your website. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to improve website speed.
d. Optimise URLs: Use descriptive URLs that make it easy for search engines to understand what each page on your website is about. Avoid using generic URLs like “page1.html”.
e. Use header tags: Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) help search engines understand the structure of your content. Use header tags to break up content into sections and highlight important keywords.
f. Use robots.txt: The robots.txt file tells search engine bots which pages they can and can’t access on your website. Make sure you’re not blocking search engines from crawling important pages.
g. Use internal linking: Internal linking helps search engines navigate your website and understand the relationship between different pages. Link to relevant pages within your website using descriptive anchor text.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve the crawlability of your website and make it easier for search engines to index your content.
4. Website Security
Website security is another important aspect of technical SEO. If your website is not secure, it can negatively impact your website’s rankings and user experience. To improve website security, you can implement the following strategies:
a. Keep software up to date: Make sure that your website’s software, including the operating system, web server, and any third-party applications, are all up to date with the latest security patches.
b. Use strong passwords: Ensure that you and your website users use strong passwords that are difficult to guess. Also, encourage users to change their passwords regularly.
c. Use SSL/TLS: Implement SSL/TLS encryption on your website to protect sensitive information such as login credentials and payment information.
d. Use a Web Application Firewall (WAF): A WAF can protect your website from common attacks, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
e. Limit access: Restrict access to your website’s administrative area and sensitive information to only authorised personnel.
f. Backup your data regularly: Regularly backup your website’s data to prevent data loss and ensure that you can recover quickly in case of a security incident.
g. Educate users: Educate your website users on safe browsing habits, such as avoiding suspicious links and not sharing sensitive information.
h. Conduct security audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and fix them before attackers can exploit them.
By taking these steps, you can significantly improve your website’s security and protect your website and its users from potential security threats.
5. Website Structure
Website structure refers to the organisation of your website’s content. A well-structured website can help search engines understand your website’s content better and improve user experience. To improve website structure, you can implement the following strategies:
a. Use a clear hierarchy: Organise your content into a clear hierarchy that makes sense to users. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to break up large blocks of text and make your content easier to read.
b. Optimise your URLs: Use descriptive and SEO-friendly URLs that include keywords related to the content on the page. Avoid using long and complex URLs that are difficult for users to remember and share.
c. Use internal linking: Link your pages together using internal links to help users navigate your site and discover related content. This also helps search engines understand the structure and content of your website.
d. Simplify your navigation: Your website should have a clear and simple navigation menu that makes it easy for users to find the information they need. Consider using drop-down menus, breadcrumbs, and other navigation aids to help users navigate your site more efficiently.
e. Use responsive design: Ensure that your website is responsive and can be viewed on different devices, such as desktops, tablets, and smartphones. This will improve the user experience and help your site rank better in search engine results.
Technical SEO is an essential aspect of website optimisation. It ensures that search engines can crawl and index your website efficiently, which can improve your website’s visibility in SERPs. To improve technical SEO, you can focus on website speed, mobile-friendliness, crawlability, website security, and website structure. By implementing these strategies, you can improve your website’s search engine rankings and user experience.

Local SEO
Local SEO is the practice of optimising a website to appear in search engine results for location-specific queries. Local SEO can be incredibly beneficial for businesses that have a physical location and want to attract more customers to their brick-and-mortar storefront. We’ll discuss the importance of local SEO, how it works, and the steps businesses can take to improve their local search rankings.
Why Local SEO is Important:
Local SEO is crucial for businesses that want to attract customers in their area. According to Google, nearly 50% of all searches have local intent. This means that people are searching for products or services in their local area. If a business isn’t optimising for local search, they’re missing out on a significant portion of potential customers.
Local SEO can also help businesses stand out from their competitors. When someone searches for a product or service in their area, Google will display a map with local businesses that match their search query. If a business appears at the top of the list, it’s more likely that the searcher will click on their website and potentially become a customer.
How Local SEO Works:
Local SEO involves a variety of tactics to improve a website’s ranking in local search results. The most important factors include:
1. Google My Business: Google My Business is a free tool that allows businesses to manage their online presence on Google, including their Google Maps listing. To optimise for local search, businesses should claim their Google My Business listing and ensure that all information, such as their address, phone number, and business hours, are accurate and up-to-date.
2. On-Page Optimisation: On-page optimisation involves optimising a website’s content to include location-specific keywords. For example, a bakery in London would want to include keywords like “London bakery” or “bakeries in London” throughout their website’s content.
3. Citations: Citations are online references to a business’s name, address, and phone number. Having consistent citations across various websites, including local directories and social media platforms, can improve a business’s local search ranking.
4. Reviews: Online reviews can also impact a business’s local search ranking. Positive reviews can help a business appear at the top of local search results, while negative reviews can have the opposite effect.
Steps to Improve Local SEO:
Improving local SEO can help your business get more visibility and attract more customers from your local area. Here are some steps you can take to improve your local SEO:
a. Claim your Google My Business (GMB) listing: Google My Business is a free tool that allows businesses to manage their online presence across Google, including search and maps. Make sure you claim your GMB listing and keep it up to date with accurate information, such as your business name, address, phone number, and business hours.
b. Optimise your GMB listing: In addition to providing accurate information, you can optimise your GMB listing by adding photos and videos, creating posts, responding to customer reviews, and enabling messaging.
c. Get listed in online directories: There are many online directories, such as Yelp, Yellow Pages, and Angie’s List, that allow businesses to list their information. Make sure your business is listed in relevant directories, and keep your information consistent across all listings.
d. Use local keywords: Use local keywords in your website content, meta descriptions, and title tags. This will help search engines understand that your business is relevant to local search queries.
e. Create local content: Create content that is relevant to your local audience, such as blog posts about local events or news. This will help attract local visitors to your website and improve your local SEO.
f. Get backlinks from local websites: Backlinks from local websites can help improve your local SEO. Reach out to local businesses and organisations to see if they would be willing to link to your website.
g. Use social media: Social media can be a great way to connect with your local audience and promote your business. Make sure you have a presence on relevant social media platforms, such as Facebook and Instagram, and post regular updates and promotions.
h. Monitor your online reputation: Monitor your online reputation and respond to customer reviews promptly, whether they are positive or negative. This will help show that you care about your customers and improve your online reputation.
By taking these steps, you can improve your local SEO and attract more local customers to your business.

Mobile SEO
In today’s digital age, mobile SEO has become an essential aspect of any online marketing strategy. With the majority of internet users accessing the web through their mobile devices, it is crucial for businesses to optimise their websites for mobile search engines. Here we will delve deeper into the concept of mobile SEO, its importance, and tips for optimising your website for mobile devices.
What is Mobile SEO?
Mobile SEO refers to the process of optimising a website’s content, structure, and other elements for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, to ensure that the website is easily accessible and readable on these devices.
Mobile SEO aims to provide the best possible user experience on mobile devices by improving website speed, navigation, and usability. It also involves optimising the website’s content for mobile devices by using responsive design, ensuring that images and videos are optimised for mobile devices, and making sure that the website is mobile-friendly.
In addition to providing a better user experience, mobile SEO is also important for search engine rankings. With more and more people using mobile devices to search the internet, search engines like Google have started to prioritise mobile-friendly websites in their search results, making mobile SEO an important part of any website’s overall SEO strategy.
Why is Mobile SEO Important?
Mobile SEO is essential because mobile devices are now the primary means of accessing the internet. Google has even switched to mobile-first indexing, meaning that it uses the mobile version of a website for ranking purposes. If your website is not optimised for mobile devices, it may not rank well in mobile search results, leading to a significant loss in traffic and potential customers.
Tips for Optimising Your Website for Mobile Devices
1. Use a Responsive Design
Responsive design is a web development approach that allows a website to adapt its layout and content to fit the screen size of different devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones. Having a responsive design is essential for mobile SEO because it improves user experience and ensures that your website is accessible and easy to use on all devices. Here are some tips for using responsive design in mobile SEO:
a. Make sure your website is mobile-friendly: Test your website using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to see if it’s optimised for mobile devices. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, you’ll need to use responsive design to make it accessible and user-friendly on mobile devices.
b. Use a responsive layout: Use a responsive layout that adjusts the size and positioning of elements on your website based on the screen size of the device. This will ensure that your website is easy to use and navigate on all devices, including smartphones.
c. Optimise images for mobile: Use images that are optimised for mobile devices. This means using smaller file sizes and choosing images that are easy to view on smaller screens.
d. Use responsive typography: Use typography that is easy to read on smaller screens. This means using font sizes that are large enough to be readable on mobile devices and using fonts that are easy to read on smaller screens.
e. Use responsive navigation: Use responsive navigation that is easy to use on mobile devices. This means using a menu that is easy to access and navigate on smaller screens.
By using responsive design in mobile SEO, you can ensure that your website is accessible and user-friendly on all devices, which will improve user experience and help your site rank higher in search engine results pages.
2. Improve Page Speed
Page speed is crucial for mobile SEO because users expect websites to load quickly on their mobile devices. Slow loading websites lead to a poor user experience, which can result in high bounce rates and low engagement. To improve your website’s page speed, consider using a content delivery network, compressing images, and minifying CSS and JavaScript files:
a. Optimise images: Large images can slow down your page speed, so optimise them by compressing the file size without compromising on quality. Use image formats such as JPEG, PNG or WebP.
b. Minimise HTTP requests: Minimise the number of HTTP requests by reducing the number of resources loaded on your page. This can be achieved by using CSS sprites, which allow you to combine multiple images into a single file.
c. Use a content delivery network (CDN): A CDN can help improve page speed by caching your website’s content on servers located closer to the user. This reduces the time it takes to load your content, resulting in faster page load times.
d. Minimise code: Minimise your code by removing unnecessary white space, comments, and code that isn’t being used. This will help reduce the size of your page and improve its load time.
e. Implement lazy loading: Lazy loading is a technique that allows your website to load only the content that is visible to the user. This reduces the number of resources that need to be loaded at once and can significantly improve page speed.
f. Use responsive design: Ensure your website is designed using a responsive design approach, which means the layout and content will automatically adjust to fit the screen size of the device being used to view it.
g. Enable browser caching: Enable browser caching to allow your website to store information in the user’s browser. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be downloaded on subsequent visits, resulting in faster page load times.
h. Use a mobile-friendly website builder: Use a website builder that is optimised for mobile devices. This will ensure that your website is optimised for mobile devices from the ground up, resulting in faster page load times.
By implementing these techniques, you can significantly improve your page speed for mobile SEO and provide a better user experience for your visitors.
3. Optimise for Mobile Keywords
Optimising for mobile keywords means using keywords that people are likely to use when searching for information on their mobile devices. This means using shorter, more concise keywords that are specific to your niche. You can use keyword research tools to find mobile-specific keywords that you can use in your content:
a. Use short-tail keywords: Mobile search queries are typically shorter than desktop ones. So, focus on using short-tail keywords that are easy to type and remember.
b. Localise your keywords: People on mobile devices are often looking for local businesses or services. So, include location-based keywords in your content to increase your visibility in local search results.
c. Focus on voice search: With the rise of smart speakers and virtual assistants, voice search is becoming increasingly popular. So, optimise your content for voice search by using natural language and long-tail keywords.
d. Prioritise mobile-friendly content: Mobile users are more likely to bounce from sites that aren’t optimised for mobile devices. So, make sure your content is easy to read and navigate on mobile devices.
e. Optimise your meta descriptions: Meta descriptions appear under your page title in search results and provide a brief summary of your content. Make sure your meta descriptions are compelling, concise, and optimised for mobile devices.
f. Use mobile-friendly formatting: Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and subheadings to make your content easier to read on mobile devices.
g. Test your website’s mobile-friendliness: Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to check your website’s mobile-friendliness and identify any issues that need to be fixed.
4. Use Mobile-Friendly Content
Mobile users consume content differently than desktop users, so it’s important to ensure that your content is easily accessible and readable on mobile devices. To create mobile-friendly content:
a. Keep your content concise: Mobile users are often on-the-go, so it’s important to keep your content short and to the point. Use bullet points, subheadings, and short paragraphs to make it easier for users to scan and digest your content.
b. Optimise images and videos: Large images and videos can slow down your website and make it difficult to load on mobile devices. Optimise your images and videos for faster loading times, and consider using smaller file sizes for mobile users.
c. Use mobile-friendly fonts: Choose fonts that are easy to read on small screens and at different font sizes. Stick to sans-serif fonts like Arial, Helvetica, and Verdana, which are easier to read on mobile devices.
d. Test your content on different devices: Test your website on different devices and screen sizes to ensure that your content is easily accessible and readable. Use tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check your website’s mobile-friendliness.
5. Optimise for Local Search
Local search is essential for businesses that serve a specific geographic location. To optimise your website for local search, ensure that your business information, such as your address, phone number, and business hours, are prominently displayed on your website. You can also use local keywords and create location-specific content to improve your local SEO rankings:
a. Claim your Google My Business listing: This is one of the most crucial steps for optimising your business for local search. Google My Business allows you to create a free listing that appears in Google’s search results when people search for businesses like yours. You can add your business name, address, phone number, website URL, hours of operation, and other relevant information to your listing.
b. Use relevant keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords into your website’s content, meta tags, and descriptions. Make sure to use local keywords that are specific to your business and its location.
c. Optimise your website for mobile: Most people use their smartphones to search for businesses near them. If your website is not mobile-friendly, it will hurt your local search rankings. Make sure your website is optimised for mobile devices.
d. Get listed in local directories: There are many local directories online, such as Yelp, Yellow Pages, and TripAdvisor. Getting listed in these directories can help improve your local search rankings.
e. Get reviews: Online reviews are critical for local businesses. Encourage your customers to leave reviews on your Google My Business listing and other review sites. Positive reviews can help improve your local search rankings.
f. Use local schema markup: Schema markup is a type of code that helps search engines understand your website’s content. Use local schema markup to help search engines understand your business’s name, address, phone number, and other important information.
g. Create local content: Creating content that is relevant to your local audience can help improve your local search rankings. Write blog posts, create videos, and share information about local events or news.
In conclusion, mobile SEO is essential for any business that wants to succeed in today’s digital age. By optimising your website for mobile devices, you can improve your SEO rankings, increase traffic, and reach more potential customers. Use the tips outlined to improve your website’s mobile SEO and take your online marketing strategy to the next level.

YouTube SEO
YouTube is the second largest search engine in the world, right after Google. Millions of people search and watch videos on YouTube every day, making it a valuable platform for businesses and content creators to reach their target audience. However, with so many videos on the platform, it can be difficult to get your content in front of the right people. That’s where YouTube SEO comes in. Here we’ll cover everything you need to know about YouTube SEO and how to optimise your videos for better visibility and engagement.
What is YouTube SEO?
YouTube SEO is the process of optimising your videos to rank higher in YouTube search results and suggested videos. The goal of YouTube SEO is to increase your visibility on the platform, attract more viewers, and ultimately grow your channel. Just like SEO for Google, YouTube SEO involves optimising various elements of your videos, including the title, description, tags, and video content itself.
Why is YouTube SEO important?
YouTube SEO is important for several reasons. First, it helps you get discovered by potential viewers who are searching for content on YouTube. If your videos are optimised for relevant keywords, they’re more likely to show up in search results, which can help you attract more viewers and grow your audience.
Second, YouTube SEO can help you rank higher in suggested videos, which are videos that YouTube recommends to viewers based on their interests and viewing history. If your videos are optimised for the right keywords and topics, they’re more likely to be recommended to viewers who are interested in your content.
Finally, YouTube SEO can help you increase engagement and watch time on your videos. If your videos are optimised for relevant keywords and topics, they’re more likely to attract viewers who are interested in your content and who are more likely to watch your videos all the way through. This can help you increase engagement and watch time, which are important factors in YouTube’s algorithm for ranking videos.
YouTube SEO Best Practices
It’s important to optimise your videos to rank well on the platform. Here are some best practices for YouTube SEO:
1. Conduct keyword research: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, YouTube’s autocomplete feature, and other keyword research tools to identify keywords and phrases that your target audience is searching for.
2. Optimise your video title: Your video title should be descriptive and include your target keyword or phrase. Keep it short and catchy to grab viewers’ attention.
3. Write a compelling video description: Your description should provide context for your video and include your target keyword. It should also encourage viewers to watch the video and provide links to relevant content.
4. Use tags wisely: Include relevant tags that describe the content of your video, but don’t overdo it. Aim for 5-10 tags that accurately describe your content.
5. Create custom thumbnails: Thumbnails are like a book cover for your video, so make sure they are high-quality and visually appealing. Use bright colours and make sure they accurately represent the content of your video.
6. Encourage engagement: Encourage viewers to like, comment, and share your video. Engagement is a key ranking factor on YouTube, so the more engagement your video gets, the better it will rank.
7. Optimise for mobile: Most people watch YouTube on their mobile devices, so make sure your videos are optimised for mobile viewing. Use large fonts, clear visuals, and keep your video length in mind.
8. Use closed captions: Closed captions improve accessibility and also help YouTube’s algorithm understand the content of your video. This can improve your video’s ranking on the platform.
9. Promote your video: Share your video on social media, embed it on your website, and include it in your email newsletters. The more views and engagement your video gets, the better it will rank on YouTube.
By following these best practices, you can improve the visibility of your YouTube videos and attract more viewers to your content.

E-commerce SEO
Unique Challenges in E-commerce SEO
E-commerce has transformed the way we shop, providing convenience and accessibility to consumers worldwide. However, for online retailers, the competitive nature of the e-commerce landscape poses unique challenges in the realm of Search Engine Optimisation (SEO). Here we explore some of the distinctive challenges faced by e-commerce websites and discuss effective strategies to overcome them.
1. Vast Product Catalogues:
Challenge:
E-commerce websites often boast extensive product catalogues, making it challenging to optimise each product page for search engines effectively.
Strategy:
Implement a well-structured hierarchy and categorisation system. Utilise concise and descriptive product titles, incorporate detailed product descriptions, and leverage product schema markup to provide search engines with rich information.
2. Dynamic Product Availability:
Challenge:
Product availability and stock levels are dynamic in the e-commerce world. Products may go out of stock, be restocked, or undergo price changes frequently.
Strategy:
Regularly update your XML sitemap and use structured data to mark up product availability, prices, and ratings. Implement 301 redirects for discontinued products and ensure a user-friendly experience with clear messaging on out-of-stock items.
3. Unique Content Challenges:
Challenge:
E-commerce websites often struggle with creating unique and compelling content for product pages, as product descriptions might be provided by manufacturers and duplicated across various online retailers.
Strategy:
Invest in creating original, engaging product descriptions. Add value by incorporating customer reviews, user-generated content, and additional information that sets your product pages apart. Prioritise quality over quantity when it comes to content.
4. Filtering and Faceted Navigation:
Challenge:
E-commerce sites commonly use filtering and faceted navigation to help users refine their product searches. However, these features can create numerous URL variations, leading to duplicate content issues.
Strategy:
Implement canonical tags to consolidate duplicate content issues arising from filtered pages. Use the robots.txt file to block search engine bots from crawling unnecessary URL parameters. Prioritise a clean URL structure for better user experience and search engine visibility.
5. Competitive Pricing and Reviews:
Challenge:
Competing in the e-commerce space often involves price wars, and product reviews play a crucial role in consumer decision-making. Balancing competitive pricing and encouraging positive reviews presents a constant challenge.
Strategy:
Focus on building a strong brand reputation and providing exceptional customer service. Encourage satisfied customers to leave reviews and respond promptly and professionally to negative feedback. Consider offering value-added services or perks rather than relying solely on price competition.
6. Mobile Optimisation:
Challenge:
With the rise of mobile commerce, optimising for mobile devices is not just a trend but a necessity. Many e-commerce websites struggle to deliver a seamless and user-friendly mobile experience.
Strategy:
Implement a responsive design that ensures a consistent experience across devices. Prioritise mobile page speed, streamline navigation, and simplify the checkout process for mobile users. Test your website regularly on various devices to identify and address any issues.
7. Complex Site Architecture:
Challenge:
Large e-commerce websites often have complex site architectures with multiple layers, categories, and subcategories, making it challenging for search engines to crawl and index efficiently.
Strategy:
Create a clear and logical site structure with a focus on user experience. Implement breadcrumb navigation, utilise internal linking strategically, and ensure that important pages are easily accessible within a few clicks. Regularly audit and update your site architecture to align with evolving business needs.
8. Security Concerns:
Challenge:
E-commerce websites handle sensitive customer information, and security is a top priority. However, security measures can sometimes inadvertently impact SEO, such as overly strict robots.txt configurations.
Strategy:
Ensure that your website’s security measures do not block essential crawling by search engines. Review and adjust your robots.txt file to allow access to critical areas, such as product pages and important content. Prioritise security without compromising search engine visibility.
E-commerce SEO comes with its unique set of challenges, but with strategic planning and implementation, these challenges can be transformed into opportunities for growth. By focusing on user experience, quality content, mobile optimisation, and effective management of product catalogues, online retailers can enhance their search engine visibility and stay ahead in the competitive e-commerce landscape. As the digital marketplace continues to evolve, adapting and refining your SEO strategies will be key to achieving sustained success in the e-commerce sector.
Product Page Optimisation
The product page serves as the digital storefront, welcoming potential customers and influencing their purchase decisions. Optimising product pages is a strategic imperative for online retailers, as it directly impacts search engine visibility, user experience, and conversion rates. Here we’ll explore key elements of product page optimisation, from compelling product descriptions to seamless navigation, and discuss strategies to enhance the overall performance of your e-commerce website.
1. Compelling Product Descriptions:
Craft Engaging and Unique Descriptions:
Effective product descriptions go beyond basic specifications. Craft compelling and unique descriptions that highlight the benefits of the product, address customer pain points, and evoke emotions. Use persuasive language to connect with your audience and encourage them to visualise the product in their lives.
Incorporate Keywords Naturally:
Integrate relevant keywords naturally into your product descriptions. Focus on long-tail keywords that reflect user intent. This not only improves search engine optimisation but also helps your product pages appear in more specific and relevant searches.
2. High-Quality Product Images:
Use High-Resolution Images:
High-quality images are essential for showcasing your products. Use high-resolution images that allow customers to zoom in and examine details. Multiple images from different angles provide a comprehensive view and instil confidence in potential buyers.
Implement Alt Text for Accessibility:
Optimise images for accessibility and search engines by adding descriptive alt text. Alt text not only aids visually impaired users but also contributes to SEO by providing context about the images on your product pages.
3. Clear Calls-to-Action (CTAs):
Design Prominent and Clear CTAs:
Guide visitors towards conversion with prominent and clear calls-to-action. Use visually appealing buttons with compelling text such as “Add to Cart” or “Buy Now.” Ensure that CTAs stand out on the page and are easily clickable.
Create a Sense of Urgency:
Encourage immediate action by incorporating elements that create a sense of urgency. Limited-time offers, countdown timers, and stock availability notifications can drive conversions by instilling a fear of missing out (FOMO).
4. User-Friendly Navigation:
Streamline Navigation:
Ensure that your product pages are part of a user-friendly navigation system. Implement clear and intuitive menus, allowing customers to easily find the products they are looking for. Breadcrumb navigation provides additional context and aids in the overall user experience.
Include Related Products and Recommendations:
Enhance user engagement by including sections for related products or personalised recommendations on each product page. This not only increases the likelihood of additional purchases but also prolongs the user’s time on your site.
5. Detailed Product Specifications:
Provide Comprehensive Specifications:
Include detailed and accurate product specifications. Outline key features, dimensions, materials, and any other relevant details. Clear and comprehensive information helps customers make informed purchasing decisions and reduces the likelihood of returns.
Utilise Structured Data Markup:
Implement structured data markup, such as schema.org, to provide search engines with additional context about your product specifications. This markup can enhance the visibility of rich snippets in search results, providing users with quick and informative previews.
6. Optimised Product URLs:
Create Clean and Descriptive URLs:
Craft clean and descriptive URLs for your product pages. Include relevant keywords and avoid using generic or automated URLs. A well-optimised URL not only improves SEO but also makes it easier for users to understand and share the link.
Avoid Duplicate Content Issues:
Be mindful of duplicate content issues that can arise from different URL parameters. Implement canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of the URL, preventing search engines from indexing multiple variations of the same product page.
7. Customer Reviews and Testimonials:
Encourage and Showcase Reviews:
Actively encourage customers to leave reviews and testimonials. Positive reviews build trust and credibility, influencing potential buyers. Showcase reviews prominently on your product pages, and consider implementing a rating system for quick visual feedback.
Respond to Customer Feedback:
Engage with customer reviews by responding promptly and professionally. Addressing concerns or expressing gratitude for positive feedback demonstrates your commitment to customer satisfaction and adds a personal touch to your online presence.
8. Responsive and Mobile-Friendly Design:
Prioritise Responsive Design:
In the era of mobile commerce, prioritise responsive design to ensure a seamless experience across devices. Test your product pages on various screen sizes, and optimise the layout and functionality for mobile users.
Optimise Page Speed for Mobile:
Mobile users expect fast-loading pages. Optimise images, minimise HTTP requests, and leverage browser caching to improve page speed on mobile devices. Consider implementing Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) for a faster and more streamlined mobile experience.
Product page optimisation is a multifaceted effort that requires attention to detail and a commitment to providing an exceptional user experience. By focusing on compelling product descriptions, high-quality images, clear CTAs, and user-friendly navigation, you can create a digital storefront that not only attracts visitors but also converts them into satisfied customers. Regularly analyse user behaviour, gather feedback, and stay abreast of industry trends to continually refine and enhance your product pages. As the e-commerce landscape evolves, a commitment to product page optimisation will be integral to your success in the competitive online marketplace.
User Experience and SEO
Where online retailers vie for the attention and loyalty of digital consumers, the synergy between User Experience (UX) and Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) is paramount. A seamless and engaging user experience not only delights visitors but also plays a crucial role in how search engines rank and prioritise websites. In this article, we’ll delve into the symbiotic relationship between e-commerce user experience and SEO, exploring key principles and strategies to enhance both aspects for sustained success in the digital marketplace.
Understanding the Nexus:
1. Page Load Speed:
User Experience: Visitors expect instant gratification. A fast-loading website contributes to a positive user experience, reducing bounce rates and keeping users engaged.
SEO Impact: Page speed is a crucial factor in search engine algorithms. Google, for instance, considers page speed when determining search rankings. A slow website can result in lower search engine visibility.
2. Mobile Optimisation:
User Experience: With the surge in mobile device usage, a mobile-optimised site is imperative. Responsive design and mobile-friendly interfaces ensure a seamless experience for users on smartphones and tablets.
SEO Impact: Google prioritises mobile-friendly websites, particularly with its mobile-first indexing approach. A mobile-optimised site contributes to higher search engine rankings, ultimately improving visibility.
3. Intuitive Navigation:
User Experience: Clear and intuitive navigation is fundamental for users to find what they need effortlessly. Well-organised menus, categories, and filters enhance the overall user experience.
SEO Impact: Search engines favour websites with logical and structured navigation. An intuitive site structure allows search engine bots to crawl and index pages efficiently, positively impacting SEO.
Optimising E-Commerce User Experience for SEO Success:
1. Mobile-First Design:
Prioritise a mobile-first design approach. Ensure that your website is not only responsive but also provides an optimised experience for users on various mobile devices. This includes streamlined navigation, touch-friendly elements, and fast-loading pages.
2. Page Speed Optimisation:
Regularly assess and optimise page load speed. Compress images, leverage browser caching, and minimise unnecessary elements that may contribute to slower load times. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to identify areas for improvement.
3. Intuitive Site Structure:
Design a clear and intuitive site structure. Categorise products logically, use descriptive URLs, and implement breadcrumb navigation. A well-organised structure not only enhances the user experience but also facilitates efficient crawling by search engine bots.
4. User-Friendly Product Pages:
Optimise product pages for both users and search engines. Craft compelling and unique product descriptions, use high-quality images, and implement schema markup to provide rich snippets in search results. Prioritise a clean and informative layout.
5. Streamlined Checkout Process:
Simplify the checkout process to minimise friction for users. A streamlined and user-friendly checkout experience contributes to higher conversion rates. Implement a guest checkout option, offer multiple payment methods, and provide clear calls-to-action.
SEO Strategies for Enhancing E-Commerce User Experience:
1. Keyword Research and Integration:
Conduct thorough keyword research to understand user search intent. Integrate relevant keywords naturally into product descriptions, titles, and meta tags. Focus on long-tail keywords that align with specific user queries.
2. Content Optimisation:
Optimise content for both users and search engines. Create valuable and informative content that addresses user needs. Utilise headers, bullet points, and engaging formatting to enhance readability. Incorporate relevant keywords to improve SEO.
3. User Reviews and Testimonials:
Actively encourage user reviews and testimonials. Positive reviews not only build trust with potential customers but also contribute to unique content on your site. Display reviews prominently on product pages, leveraging both social proof and SEO benefits.
4. Structured Data Markup:
Implement structured data markup (schema.org) to provide search engines with additional context about your content. This markup can result in rich snippets in search results, offering users more information before they click through to your site.
5. Internal Linking Strategy:
Develop a strategic internal linking strategy. Link relevant pages within your site to guide users to related products or content. Internal linking aids in navigation and also distributes link equity, contributing to SEO.
Fostering Harmony for E-Commerce Success
The intertwining relationship between e-commerce user experience and SEO is undeniable. A positive user experience not only satisfies customers but also aligns with the criteria search engines use to determine rankings. By prioritising mobile optimisation, page speed, intuitive navigation, and user-friendly product pages, you create a foundation for both user satisfaction and SEO success.
Striking the right balance between an intuitive, user-centric design and SEO best practices ensures that your e-commerce website not only attracts visitors but also retains and converts them into loyal customers. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, embracing this symbiotic relationship is essential for achieving and sustaining success in the competitive e-commerce marketplace.

SEO Analytics
Setting Up Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that provides invaluable insights into the performance of your website, helping you understand visitor behaviour, track conversions, and make data-driven decisions to enhance your online presence. Setting up Google Analytics is a fundamental step for any website owner or digital marketer. Here we walk you through the process of setting up Google Analytics to ensure you’re equipped with the essential tools for monitoring and optimising your online performance.
Step 1: Sign Up for Google Analytics
Go to the Google Analytics website:
Navigate to Google Analytics and sign in with your Google account. If you don’t have a Google account, you’ll need to create one.
Create a new account:
Click on “Start for free” and follow the prompts to set up a new Google Analytics account. Provide your account name, website name, URL, industry category, and time zone.
Choose a data sharing setting:
Decide whether you want to share your data with Google to help improve Google Analytics. Make your selection and click “Next.”
Accept the terms of service:
Read and accept the terms of service and click “I Accept.”
Step 2: Set Up a Property in Google Analytics
Create a new property:
After setting up your account, you’ll need to create a property for your website. Click on “Create Property” and provide your website name, URL, and industry category.
Choose your platform:
Select the platform your website is built on (e.g., web, app) and click “Next.”
Configure your data stream (if applicable):
If you’re setting up an app, you’ll need to configure a data stream. Follow the prompts to complete this step.
Configure additional settings:
Provide additional information such as your time zone and currency, and click “Create.”
Step 3: Get Your Tracking Code
Accept the data sharing settings:
Choose your data sharing settings for this property and click “Save.”
Get your tracking code:
On the next screen, you’ll see your tracking code. Copy the entire Global Site Tag (gtag.js) code.
Step 4: Implement the Tracking Code on Your Website
Add the tracking code to your website:
Paste the copied tracking code into the header section of every page on your website. This can be done manually by editing your website’s HTML or by using a website platform that allows you to add tracking codes.
Verify the installation:
After adding the tracking code, go back to Google Analytics and click “Next.” Google Analytics will verify the installation. This process may take some time.
Step 5: Explore Google Analytics Dashboard
Access your dashboard:
Once the tracking code is verified, you’ll be directed to your Google Analytics dashboard. Here, you’ll find a wealth of information about your website’s performance.
Navigate the dashboard:
Familiarise yourself with the various sections of the dashboard, including Realtime, Audience, Acquisition, Behaviour, and Conversions. Each section provides insights into different aspects of your website’s performance.
Step 6: Set Up Goals and Conversions
Define your goals:
Go to the “Admin” section in Google Analytics and navigate to the “Goals” tab. Here, you can set up specific goals that align with your business objectives, such as form submissions, newsletter sign-ups, or product purchases.
Configure e-commerce tracking (if applicable):
If you run an e-commerce website, consider enabling e-commerce tracking to gain insights into your sales performance. This involves additional setup in the “Admin” section under “E-commerce Settings.”
Step 7: Configure Additional Settings
Explore advanced settings:
In the “Admin” section, you’ll find additional settings that allow you to configure user permissions, link to other Google products, and set up filters to exclude certain data from your reports.
Customise your dashboard:
Customise your dashboard to display the metrics and reports that matter most to you. This can be done by clicking on “Customisation” in the left navigation bar.
Step 8: Monitor and Analyse
Regularly review reports:
Make it a habit to regularly review the reports in Google Analytics. Monitor user behaviour, traffic sources, and the performance of your goals and conversions.
Adjust and optimise:
Use the insights gained from Google Analytics to make informed decisions about your website’s content, marketing strategies, and user experience. Continuously optimise your site based on data-driven findings.
Empowering Your Online Success
Setting up Google Analytics is a foundational step in unlocking the full potential of your website. By leveraging the insights provided by this powerful tool, you can make informed decisions to enhance user experience, drive traffic, and achieve your business goals. Regularly explore new features and updates in Google Analytics to stay ahead of industry trends and continuously refine your digital strategy. With a well-configured Google Analytics account, you’ll be empowered to navigate the digital landscape and propel your online success.
Monitoring Key SEO Metrics
Effective monitoring of SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) metrics is essential for the success of any online venture. SEO metrics provide valuable insights into the performance of your website, helping you gauge its visibility, user engagement, and overall health in the eyes of search engines. We’ll explore key SEO metrics, why they matter, and how to monitor them to drive continuous improvement in your online presence.
1. Organic Traffic: The Foundation of SEO Success
Why it Matters:
Organic traffic represents the number of visitors who find your website through non-paid (organic) search results. Monitoring organic traffic is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of your SEO efforts in attracting users through search engines.
How to Monitor:
Google Analytics: Navigate to the “Acquisition” section in Google Analytics and select “Organic Search.” Here, you can track the number of organic sessions, pageviews, and other relevant metrics.
2. Keyword Rankings: Unveiling Search Visibility
Why it Matters:
Keyword rankings reveal where your website appears in search engine results for specific terms. Monitoring keyword rankings helps you understand your site’s visibility and identify areas for improvement.
How to Monitor:
SEO Tools: Utilise SEO tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Moz to track your keyword rankings. These tools provide insights into your current rankings, changes over time, and potential opportunities for optimisation.
3. Click-Through Rate (CTR): Navigating User Engagement
Why it Matters:
CTR represents the percentage of users who click on your website’s link in search results. A high CTR indicates that your content is relevant and compelling to users.
How to Monitor:
Google Search Console: Access the Performance report in Google Search Console to view your pages’ CTR. Analyse the CTR data for individual pages and identify opportunities to enhance meta titles and descriptions.
4. Bounce Rate: Retaining Visitor Engagement
Why it Matters:
Bounce rate reflects the percentage of visitors who navigate away from your site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate may signal issues with user experience or content relevance.
How to Monitor:
Google Analytics: Examine the bounce rate in Google Analytics under the “Behaviour” section. Identify pages with high bounce rates and assess whether improvements to content or navigation are needed.
5. Page Load Speed: Enhancing User Experience
Why it Matters:
Page load speed directly impacts user experience and SEO. Slow-loading pages can result in higher bounce rates and lower search engine rankings.
How to Monitor:
Google PageSpeed Insights: Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to analyse the loading speed of your web pages. Address recommendations to optimise images, leverage browser caching, and enhance overall page speed.
6. Backlink Profile: Building Authority
Why it Matters:
Backlinks, or incoming links from other websites, contribute to your site’s authority and search engine rankings. Monitoring your backlink profile helps you identify quality links and address potentially harmful ones.
How to Monitor:
Backlink Analysis Tools: Utilise backlink analysis tools such as Ahrefs, Majestic, or Moz to assess the quality and quantity of your backlinks. Keep an eye on new links, lost links, and overall trends.
7. Conversion Rate: Measuring Goal Success
Why it Matters:
Conversion rate measures the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, filling out a form, or signing up for a newsletter. It directly ties back to the success of your business goals.
How to Monitor:
Google Analytics: Track conversion rates in Google Analytics by setting up goals or e-commerce tracking. Monitor the performance of specific pages and campaigns to optimise for conversions.
8. Mobile Responsiveness: Catering to Mobile Users
Why it Matters:
With the prevalence of mobile device usage, mobile responsiveness is crucial for both user experience and SEO. Google prioritises mobile-friendly websites in its rankings.
How to Monitor:
Google Mobile-Friendly Test: Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to assess whether your website meets mobile responsiveness standards. Address any issues identified to ensure a seamless mobile experience.
9. Crawling and Indexing: Ensuring Visibility
Why it Matters:
Search engines must crawl and index your pages to display them in search results. Monitoring crawling and indexing issues helps identify obstacles that may hinder your site’s visibility.
How to Monitor:
Google Search Console: Check the “Coverage” report in Google Search Console to identify indexing issues. Address errors, warnings, and excluded pages to ensure comprehensive search engine coverage.
10. Social Signals: Amplifying Reach
Why it Matters:
Social signals, such as likes, shares, and comments on social media platforms, can impact your website’s visibility in search results. They indicate social engagement and brand authority.
How to Monitor:
Social Media Analytics: Use analytics tools provided by social media platforms to track engagement metrics. Analyse trends in social signals and tailor your content strategy based on audience preferences.
A Holistic Approach to SEO Monitoring
Monitoring key SEO metrics is not a one-time task but an ongoing process that requires attention and adaptation. A holistic approach to SEO monitoring involves regularly assessing a diverse set of metrics, identifying trends, and implementing strategic optimisations based on insights gained. By staying vigilant and responsive to changes in the digital landscape, you empower your website to not only meet current SEO standards but also thrive in the ever-evolving online environment.
Conversion Tracking
Conversion tracking is the compass that guides marketers, helping them navigate the intricate landscape of online campaigns, analyse user behaviour, and measure the effectiveness of their strategies. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the importance of conversion tracking, explore various types of conversions, and provide a roadmap for setting up and optimising conversion tracking for your digital initiatives.
The Significance of Conversion Tracking
Defining Conversions:
A conversion occurs when a visitor takes a desired action on your website, such as making a purchase, submitting a form, or signing up for a newsletter. Understanding and tracking these actions are fundamental to evaluating the success of your online efforts.
Why Conversion Tracking Matters:
Performance Measurement: Conversion tracking serves as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of your marketing channels. It allows you to identify which campaigns, channels, or keywords are driving valuable actions.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Armed with conversion data, marketers can make informed decisions. Analysing what works and what doesn’t enables strategic adjustments to maximise return on investment (ROI).
Optimising User Experience: Conversion tracking sheds light on user behaviour, highlighting the paths users take to reach conversion points. This insight is invaluable for optimising user experience and streamlining the conversion journey.
Budget Allocation: Effective conversion tracking helps allocate budget wisely. By identifying high-performing channels and campaigns, marketers can allocate resources to areas that yield the best results.
Types of Conversions
Macro Conversions:
Macro conversions represent significant actions that align with primary business goals. Examples include:
- Purchase Transactions: Completing an online purchase.
- Lead Generation Forms: Submitting contact forms or inquiry forms.
- Account Sign-Ups: Registering for an account on a platform.
Micro Conversions:
Micro conversions are smaller, but still valuable, actions that contribute to the overall user journey. Examples include:
- Email Sign-Ups: Subscribing to newsletters.
- Content Downloads: Accessing whitepapers, ebooks, or guides.
- Video Views: Watching product or informational videos.
Setting Up Conversion Tracking: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Define Your Goals:
Clearly define your business goals and the corresponding actions you want users to take on your website. These goals will serve as the foundation for your conversion tracking setup.
2. Utilise Google Analytics:
If you’re not already using Google Analytics, set up an account and integrate it with your website. Google Analytics provides a robust platform for tracking various types of conversions.
3. Establish Conversion Goals:
In Google Analytics, navigate to the “Admin” section, and under the “View” column, click on “Goals.” Create new goals that align with your defined conversions. Specify goal details, such as the destination page or event.
4. Implement E-commerce Tracking (if applicable):
If your website involves e-commerce, activate e-commerce tracking in Google Analytics. This allows you to track transaction data, revenue, and other valuable metrics related to online purchases.
5. Set Up Conversion Tracking in Advertising Platforms:
For paid advertising campaigns, each major advertising platform (Google Ads, Facebook Ads, etc.) provides tools for setting up conversion tracking. Generate and implement the unique tracking codes on your website.
6. Utilise Event Tracking:
For tracking interactions that are not page loads, such as clicks on specific buttons or form submissions, implement event tracking. Google Tag Manager is a powerful tool for setting up event tracking without the need for code changes.
7. Test and Verify:
After implementing conversion tracking, thoroughly test its functionality. Ensure that each conversion is accurately recorded in your analytics platform. This step is crucial for reliable data collection.
Optimising Conversion Tracking
Regular Analysis:
Periodically review your conversion data. Identify trends, seasonal variations, and any anomalies that may impact your strategy. Regular analysis provides insights into the effectiveness of your campaigns.
A/B Testing:
Conduct A/B testing to refine and optimise your campaigns. Test variations of ad copy, landing pages, and calls-to-action to determine which elements resonate most effectively with your audience.
Conversion Rate Optimisation (CRO):
Implement conversion rate optimisation strategies to enhance the likelihood of conversions. This may involve improving website design, streamlining checkout processes, or refining the messaging on your landing pages.
Attribution Modelling:
Explore different attribution models to understand the various touchpoints in a user’s journey that contribute to conversions. Attribution modelling helps distribute credit to different channels, providing a more holistic view of the customer journey.
User Feedback:
Gather feedback from users through surveys, reviews, or direct communication. Understanding user perspectives can reveal insights into potential barriers to conversions and guide optimisation efforts.
Empowering Success Through Insightful Tracking
Conversion tracking is the compass that guides your digital voyage, providing insights into the effectiveness of your campaigns and helping you steer towards success. By defining, implementing, and optimising conversion tracking, you equip yourself with the tools needed to understand user behaviour, refine strategies, and continually improve the impact of your online initiatives. As the digital landscape evolves, the ability to harness conversion data becomes increasingly crucial for businesses striving to thrive in the competitive online arena.

SEO Reporting
SEO reporting stands as a compass guiding businesses toward online success. Reporting not only quantifies the impact of SEO efforts but also provides valuable insights for strategic decision-making. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the significance of SEO reporting, the essential components of a comprehensive report, and effective strategies for communicating SEO performance.
The Significance of SEO Reporting
1. Quantifying Impact:
SEO reporting transforms abstract strategies into tangible results. It quantifies the impact of optimisation efforts, offering a clear picture of how changes have influenced website visibility, traffic, and conversions.
2. Strategic Decision-Making:
Informed decision-making is the cornerstone of successful digital strategies. SEO reports provide the data necessary to refine tactics, allocate resources effectively, and adapt to evolving trends in the digital landscape.
3. Accountability and Transparency:
For businesses working with SEO agencies or in-house teams, reporting fosters accountability and transparency. Stakeholders can assess the value of SEO investments and gain confidence in the strategies being implemented.
Components of a Comprehensive SEO Report
1. Executive Summary:
An executive summary provides a high-level overview of key metrics and accomplishments. It’s designed for busy stakeholders who need a quick snapshot of SEO performance without delving into detailed data.
2. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Identify and highlight key performance indicators relevant to the business goals. Common KPIs include organic traffic, keyword rankings, conversion rates, and backlink growth. Tailor KPIs to align with specific objectives.
3. Traffic Analysis:
Dive into organic traffic metrics to understand how users are finding and interacting with the website. Break down traffic sources, analyse user behaviour, and identify trends that may impact SEO strategy.
4. Keyword Performance:
Evaluate the performance of target keywords. Track rankings, assess changes over time, and identify opportunities for optimisation. Keyword performance data provides insights into the effectiveness of content strategies.
5. Conversion Metrics:
Connect SEO efforts to business outcomes by including conversion metrics. Track goals, lead generation forms, and e-commerce transactions influenced by organic search. This ties SEO directly to the bottom line.
6. Technical SEO Audit:
Include a summary of technical SEO aspects, such as website speed, mobile responsiveness, and crawlability. Identify and address technical issues that may impact search engine rankings.
7. Backlink Profile:
Analyse the backlink profile to assess the quality and quantity of incoming links. Highlight new backlinks, monitor the anchor text distribution, and identify opportunities for building authority.
8. Competitor Analysis:
Provide insights into the competitive landscape. Analyse competitor rankings, strategies, and changes that may impact your own approach. Understanding the competitive context helps refine SEO strategies.
9. Content Performance:
Evaluate the performance of content assets. Identify top-performing pages, assess engagement metrics, and uncover content gaps. Content performance data guides content creation and optimisation efforts.
10. Recommendations and Action Plan:
Conclude the report with clear recommendations and an action plan. Highlight areas for improvement, strategic adjustments, and upcoming initiatives. The action plan serves as a roadmap for ongoing optimisation.
Effective Strategies for Communicating SEO Performance
1. Clarity and Simplicity:
Present data in a clear and simple manner. Use visuals, charts, and graphs to make complex information easily digestible. Avoid jargon that may confuse stakeholders.
2. Alignment with Business Goals:
Relate SEO metrics directly to business goals. Demonstrate how SEO efforts contribute to increased revenue, lead generation, or brand visibility. This alignment reinforces the value of SEO in achieving broader objectives.
3. Contextualisation of Data:
Provide context for the data presented. Explain the significance of fluctuations, trends, or anomalies. Contextualising data helps stakeholders understand the broader implications of performance metrics.
4. Regular Reporting Cadence:
Establish a regular reporting cadence. Whether monthly, quarterly, or on a custom schedule, consistent reporting builds trust and allows stakeholders to track progress over time.
5. Customisation for Different Audiences:
Tailor reports for different audiences. Executives may require a high-level summary, while marketing teams may benefit from more detailed insights. Customise reporting to meet the specific needs of each stakeholder.
6. Education and Insight Sharing:
Take the opportunity to educate stakeholders about SEO concepts and strategies. Share insights about industry trends, algorithm updates, and the evolving nature of search engines. Informed stakeholders are better equipped to support SEO initiatives.
Elevating Performance Through Insightful Reporting
In the intricate landscape of digital marketing, SEO reporting is more than a routine task—it’s a strategic imperative. By providing a comprehensive view of performance, SEO reports empower businesses to optimise strategies, allocate resources wisely, and navigate the ever-changing terrain of online visibility. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the ability to communicate and leverage SEO insights through effective reporting becomes a cornerstone of sustained success.

SEO Algorithm Updates and Trends
With search engines continually refining their algorithms to enhance user experience and deliver more relevant results. Staying ahead of the curve in the realm of SEO requires a keen understanding of the latest algorithm updates and emerging trends. Here we discuss the key aspects of SEO algorithm updates and trends that businesses and digital marketers need to be aware of in order to maintain and improve their online visibility.
The Importance of SEO Algorithm Updates:
Enhancing User Experience:
Search engines like Google regularly update their algorithms to prioritise websites that provide a positive user experience. Factors such as page speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall website usability play a crucial role in these updates.
Content Relevance and Quality:
Algorithms are designed to assess the relevance and quality of content. Fresh and valuable content is favoured, and websites that consistently produce high-quality, informative content tend to rank higher in search results.
E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness):
Google, in particular, emphasises E-A-T as a ranking factor. Websites are evaluated based on the expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness of their content and overall online presence.
Recent Algorithm Updates:
Core Updates:
Google regularly releases core algorithm updates, impacting a broad range of websites. These updates focus on refining the overall search algorithm and may result in significant changes in rankings.
Page Experience Update:
With the Page Experience update, Google places a strong emphasis on user-centric metrics like Core Web Vitals, which include factors such as page loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
Bert Algorithm:
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) is designed to improve the understanding of context in search queries. It enables search engines to comprehend the nuances of language, providing more accurate and relevant search results.
Emerging Trends in SEO:
Voice Search Optimisation:
The increasing prevalence of voice-activated devices has led to a rise in voice searches. Optimising content for conversational queries and long-tail keywords is becoming crucial for maintaining visibility in voice search results.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
AI and machine learning are shaping the future of SEO. Search engines use AI to better understand user intent, personalise search results, and identify patterns in user behaviour.
Video Content Optimisation:
Video content is gaining prominence in search results. Optimising video content for search engines, utilising relevant keywords and providing detailed descriptions, can significantly enhance visibility.
Mobile-First Indexing:
As mobile device usage continues to rise, search engines prioritise mobile-friendly websites. Mobile-first indexing means that the mobile version of a site is considered the primary version for indexing and ranking.
Staying informed about algorithm updates and emerging trends is essential for maintaining a strong online presence. Businesses and digital marketers must adapt their strategies to align with the evolving criteria set by search engines. By focusing on user experience, content quality, and embracing new technologies, organisations can navigate the complex world of SEO and ensure their websites rank prominently in search engine results.

International SEO
In our interconnected world, businesses are expanding their reach beyond borders, aiming to tap into the vast potential of international markets. With this globalisation trend comes the crucial need for a robust International SEO strategy. International SEO goes beyond traditional SEO practices, considering linguistic, cultural, and geographical nuances to ensure a website’s visibility and success on a global scale.
Understanding the Basics:
Keyword Research:
Conducting thorough keyword research is the foundation of any successful SEO strategy. In an international context, this involves identifying relevant keywords in different languages and regions.
Utilise tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to identify high-volume and culturally appropriate keywords for your target audience.
Hreflang Tags:
Implementing hreflang tags is crucial for signalling to search engines the language and regional targeting of your content. This helps search engines deliver the most relevant content to users based on their location and language preferences.
Incorrect implementation of hreflang tags can lead to content confusion and impact search rankings negatively.
Technical Considerations:
Website Structure:
Design your website structure to cater to an international audience. Consider using country-specific top-level domains (ccTLDs) or subdirectories for different language versions.
Ensure that your website’s URL structure is logical and follows a clear hierarchy, making it easy for search engines to crawl and index.
Site Speed and Accessibility:
International audiences may access your site from various locations, so optimising site speed is crucial. Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to distribute content across multiple servers globally and improve loading times.
Ensure your website is accessible and user-friendly for audiences with different devices and network conditions.
Content Localisation:
Multilingual Content:
Tailor your content to the linguistic and cultural preferences of your target audience. Avoid simply translating content; instead, localise it to resonate with the cultural context of each region.
Hire native speakers or professional translators to ensure the quality and accuracy of translated content.
Cultural Sensitivity:
Understand the cultural nuances of your target markets. Certain phrases, images, or colours may have different meanings in various regions. Adapt your content to avoid misunderstandings and resonate with local audiences.
Link Building and Outreach:
Local Link Building:
Establish a strong backlink profile by engaging in local link-building activities. Partner with reputable local businesses, industry influencers, or organisations to build credibility and authority in each target market.
Leverage social media platforms and local online communities to connect with your international audience.
Social Media Localisation:
Customise your social media strategy for each region. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter offer localisation features that allow you to tailor content for different audiences.
Engage with local communities and participate in relevant conversations to build a strong social media presence.
Monitoring and Analytics:
International SEO Metrics:
Monitor the performance of your international SEO efforts by tracking key metrics such as organic traffic, keyword rankings, and conversion rates in each target market.
Use tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and other SEO analytics platforms to gain insights into the effectiveness of your strategy.
Regular Audits:
Conduct regular SEO audits to identify and address any issues that may arise. This includes checking for broken links, outdated content, and technical issues that could affect your website’s performance in international search results.
Mastering the art of International SEO is essential for businesses looking to thrive in a global marketplace. By understanding the intricacies of different languages, cultures, and search engine algorithms, you can optimise your website to reach and engage audiences worldwide. Remember that the key to successful international expansion lies in continuous adaptation, monitoring, and a commitment to delivering a seamless and culturally relevant online experience.

SEO Best Practices
When studying the different types of SEO, we also have to consider the various strategies and techniques used including White Hat SEO, Gray Hat SEO and Black Hat SEO, and know the advantages, characteristics and risks that you face are dependent on which of these you use. We will start by discussing these strategies and techniques:
White-Hat SEO
This approach has gained widespread recognition and acceptance and focuses on providing high-quality content, using relevant keywords, and improving website usability to provide the best possible user experience.
What is White-Hat SEO?
White-Hat SEO refers to the use of ethical and legitimate techniques to improve a website’s search engine rankings. This includes optimising a website’s content and structure in accordance with search engine guidelines, as opposed to using manipulative or deceptive tactics to achieve higher rankings. White-Hat SEO can include activities such as keyword research, on-page optimisation, link building, and content creation.
Why is White-Hat SEO Important?
White-Hat SEO is important for several reasons. First and foremost, it helps to ensure that your website is not penalised or banned by search engines for engaging in unethical or manipulative practices. This can have serious consequences for your online visibility and reputation, and can even result in legal action in some cases.
Secondly, White-Hat SEO is more sustainable and effective in the long run than Black-Hat SEO techniques. While Black-Hat SEO tactics may provide short-term gains, they are likely to be penalised by search engines in the long run, resulting in a significant loss of traffic and revenue.
Finally, White-Hat SEO helps to build a positive and trustworthy online reputation for your website and brand. By following ethical and transparent SEO practices, you can establish yourself as a reliable and credible source of information, which can lead to increased traffic, conversions, and customer loyalty.
How to Use White-Hat SEO to Improve Your Website’s Search Engine Rankings
Here are some key White-Hat SEO techniques you can use to improve your website’s search engine rankings:
1. Conduct Keyword Research: Keyword research is the foundation of any effective SEO strategy. By identifying the most relevant and valuable keywords for your niche or industry, you can optimise your content and structure to better meet the needs and expectations of your target audience. There are many different tools and techniques available for conducting keyword research, including Google Keyword Planner, SEMRush, and Ahrefs.
2. Optimise Your On-Page Content: On-page optimisation involves optimising the content and structure of your website’s individual pages to make them more search engine friendly. This includes optimising your page titles, headings, meta descriptions, and content to include relevant keywords and information. On-page optimisation can also include optimising your website’s structure and navigation to make it easier for search engines and users to find and navigate your content.
3. Build Quality Backlinks: Backlinks are links from other websites to your own website, and they are an important factor in search engine rankings. However, not all backlinks are created equal. Quality backlinks come from authoritative and trustworthy websites that are relevant to your niche or industry. You can build quality backlinks through guest posting, influencer outreach, and other link building strategies.
4. Create High-Quality Content: Content is king in the world of SEO, and creating high-quality, informative, and engaging content is essential for improving your search engine rankings. This can include blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, and other types of content that provide value and relevance to your target audience.
5. Monitor Your Progress and Adapt Your Strategy: SEO is an ongoing process, and it’s important to monitor your progress and adapt your strategy as needed. This can involve tracking your website’s rankings, analysing your traffic and conversion rates, and making changes to your content, structure, and optimisation techniques based on your findings.
White-Hat SEO is a crucial aspect of any effective digital marketing strategy. By following ethical and legitimate optimisation techniques, you can improve your website’s search engine rankings, build a positive online reputation, and attract more traffic, conversions, and customers to your website. Remember to conduct keyword research, optimise your on-page content, build quality backlinks, create high-quality content, and monitor your progress and adapt your strategy as needed. With patience, persistence, and a commitment to ethical SEO practices, you can achieve sustainable success in the ever-changing world of search engine optimisation.
Black-Hat SEO
Some businesses and marketers use unethical tactics to improve their rankings, known as black-hat SEO. Here we’ll define black-hat SEO, discuss why it’s harmful, and provide tips on how to avoid it.
What is Black-Hat SEO?
Black-hat SEO refers to unethical tactics used to manipulate search engine rankings and deceive search engines into ranking a website higher than it should be. These tactics violate search engine guidelines and can lead to penalties, including lower search engine rankings or even removal from search engine results pages.
Some common black-hat SEO tactics include:
1. Keyword stuffing: This involves overloading a website’s content with keywords to manipulate search engine rankings. It’s often done by adding irrelevant or repetitive keywords to a website’s content or meta tags.
2. Cloaking: This tactic involves showing search engines different content than what is shown to users. It’s often done by using code to display content that’s optimised for search engines, while hiding the actual content from users.
3. Paid links: This involves buying links from other websites to improve a website’s ranking. However, search engines consider paid links to be a violation of their guidelines.
4. Hidden text: This involves hiding text on a website that’s only visible to search engines. It’s often done by using a font colour that matches the background colour or by using CSS to hide the text.
Why is Black-Hat SEO Harmful?
Black-hat SEO is harmful for several reasons. First, it violates search engine guidelines and can lead to penalties, including lower search engine rankings or even removal from search engine results pages. This can be devastating for businesses that rely on search engine traffic to drive sales and revenue.
Second, black-hat SEO tactics can also harm the user experience. Keyword stuffing, for example, can make a website’s content difficult to read and lower the quality of the content. Cloaking can also deceive users by showing them different content than what they expected.
Finally, black-hat SEO can also harm a business’s reputation. If a business is caught using black-hat SEO tactics, it can damage their brand and make it difficult to regain the trust of customers and search engines.
How to Avoid Black-Hat SEO
The best way to avoid black-hat SEO is to focus on white-hat SEO tactics that are ethical and comply with search engine guidelines. Black-hat SEO is a harmful practice that can lead to penalties, harm the user experience, and damage a business’s reputation. It’s important for businesses to focus on ethical SEO tactics that comply with search engine guidelines. By creating high-quality content, conducting keyword research, building backlinks, and optimising website structure, businesses can improve their search engine rankings and drive more traffic to their website, all while maintaining their reputation and trust with customers.
Gray-Hat SEO
While there are ethical “White-Hat” SEO techniques that follow search engine guidelines, and unethical “Black-Hat” SEO techniques that violate search engine guidelines, there is also a gray area in between. This gray area is known as Gray-Hat SEO. Here we will explore what Gray-Hat SEO is, the techniques used, the risks involved, and best practices to follow.
What is Gray-Hat SEO?
Gray-Hat SEO refers to SEO techniques that fall somewhere between White-Hat SEO and Black-Hat SEO. While Gray-Hat SEO tactics may not necessarily be illegal or unethical, they are often considered to be somewhat risky or dubious. Some common Gray-Hat SEO techniques include:
1. Guest Posting: Guest posting involves writing articles for other websites with a link back to your own website. While guest posting is generally considered a legitimate White-Hat SEO technique, it can be considered a Gray-Hat technique if the articles are of low quality or the links are from low-quality websites.
2. Paid Links: Paid links involve paying other websites to include a link back to your own website. While paying for links is against Google’s guidelines, it is not illegal. However, paid links can be considered a Gray-Hat technique if they are not disclosed to search engines and are not relevant or high-quality.
3. Keyword Stuffing: Keyword stuffing involves including a large number of keywords in the content of a website with the aim of manipulating search engine rankings. While this technique is a clear violation of search engine guidelines and considered Black-Hat SEO, some Gray-Hat SEO practitioners may use keyword stuffing in a more subtle or limited way.
4. Link Exchanges: Link exchanges involve trading links with other websites in order to boost search engine rankings. While link exchanges are generally considered to be a White-Hat SEO technique, they can be considered a Gray-Hat technique if the links are from low-quality or irrelevant websites.
The Risks of Gray-Hat SEO
While Gray-Hat SEO techniques may not be explicitly illegal or unethical, they can put a website at risk of being penalised by search engines. Google’s algorithms are constantly evolving to detect and penalise websites that use manipulative techniques to boost search engine rankings. Websites that use Gray-Hat SEO techniques may see a temporary boost in search engine rankings, but this boost may be short-lived as search engines catch up and penalise them. In some cases, websites that use Gray-Hat SEO techniques may even be completely removed from search engine results pages (SERPs).
Best Practices for Gray-Hat SEO
If you are considering using Gray-Hat SEO techniques, it is important to proceed with caution and follow best practices to minimise the risk of penalties. Here are some best practices for Gray-Hat SEO:
a. Focus on Quality: Regardless of the SEO technique you use, always prioritise quality. Ensure that your content is valuable and relevant to your audience, and that any links you include are from high-quality and relevant websites.
b. Be Transparent: If you use any Gray-Hat SEO techniques, be transparent about it. For example, if you pay for links, disclose this to search engines by using the rel=”nofollow” attribute on the links.
c. Monitor Your Rankings: Keep a close eye on your search engine rankings and traffic. If you notice any sudden drops, it may be a sign that you have been penalised. Address the issue immediately by identifying and removing any Gray-Hat SEO techniques that may be causing the penalty.
d. Diversify Your SEO Strategy: Don’t rely solely on Gray-Hat SEO techniques. Instead, diversify your SEO strategy by using a combination of White-Hat and Gray-Hat SEO techniques, as well as other marketing channels such as social media and content marketing.
e. Stay Up-to-Date with Search Engine Guidelines: Make sure you stay up-to-date with search engine guidelines and algorithms. Google regularly updates its algorithms to detect and penalise manipulative SEO techniques, so it is important to stay informed and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Gray-Hat SEO techniques can be tempting for website owners who want to achieve higher search engine rankings quickly. However, these techniques come with significant risks and should be used with caution. By following best practices and focusing on quality, transparency, monitoring, diversification, and staying up-to-date with search engine guidelines, you can minimise the risk of penalties and achieve long-term SEO success.

Artificial Intelligence in SEO
With the advent of artificial intelligence (AI), SEO has undergone a transformative journey, redefining the way businesses optimise their online presence. AI, with its ability to analyse vast datasets, understand user behaviour, and adapt to dynamic search engine algorithms, has become an indispensable tool for modern SEO strategies.
Data Analysis and Insights:
AI plays a crucial role in processing and analysing enormous amounts of data that are integral to SEO. Through machine learning algorithms, AI tools can quickly identify patterns, trends, and correlations within datasets that would be challenging for humans to discern manually. This enables SEO professionals to gain valuable insights into user behaviour, keyword trends, and content performance.
Content Creation and Optimisation:
One of the most significant impacts of AI in SEO is its role in content creation and optimisation. Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms empower AI to understand context, semantics, and user intent. Content generated by AI can be tailored to align with the preferences of search engines and user expectations, enhancing its relevance and discoverability. Additionally, AI tools assist in optimising existing content by identifying opportunities for improvement based on evolving search engine algorithms.
Personalised User Experience:
AI-driven personalisation has become a game-changer in SEO. By analysing user behaviour, preferences, and historical data, AI algorithms can deliver personalised content and recommendations. This not only enhances user satisfaction but also contributes to lower bounce rates and increased engagement, factors that search engines consider when ranking websites.
Voice Search Optimisation:
As voice search continues to gain popularity, AI is instrumental in optimising content for this medium. Voice search queries are inherently more conversational, and AI-driven tools assist in understanding and adapting to the nuances of spoken language. This ensures that websites are well-optimised for voice search, a crucial aspect of modern SEO.
Algorithmic Changes and Adaptability:
Search engine algorithms are constantly evolving, and staying ahead of these changes is essential for maintaining a strong online presence. AI enables SEO professionals to adapt quickly to algorithmic shifts by analysing changes and adjusting strategies accordingly. This adaptability is particularly crucial in an era where search engines prioritise factors like user experience, relevance, and quality content.
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting:
AI’s predictive analytics capabilities empower SEO professionals to anticipate future trends and changes in user behaviour. By analysing historical data, AI tools can provide forecasts and insights that guide strategic decision-making. This proactive approach allows businesses to stay ahead of the competition and adjust their SEO strategies accordingly.
In the modern era of SEO, artificial intelligence has become a powerful ally, offering insights, automation, and adaptability that were once unimaginable. The integration of AI into SEO strategies not only streamlines processes but also enhances the overall effectiveness of digital marketing efforts. As search engines continue to prioritise user experience and relevance, the role of AI in SEO is set to become even more integral in shaping the online success of businesses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) is a multifaceted field that demands a profound comprehension of search engine algorithms and user behaviour. The employment of various techniques such as White Hat SEO, Gray Hat SEO, and Black Hat SEO can significantly impact website rankings and user experience. On-page SEO, Off-page SEO, and Technical SEO serve as pivotal components that enable the optimisation of websites for search engines, ultimately enhancing user engagement.
Moreover, incorporating strategies like Local SEO, Mobile SEO, and YouTube SEO can contribute to bolstering businesses’ online presence and visibility within specific search results. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of the latest trends and adhering to best practices remains imperative for success in the dynamic realm of SEO.
In this ever-changing landscape, the integration of AI technologies has become increasingly essential. AI not only plays a significant role in deciphering complex search engine algorithms but also aids in automating certain aspects of SEO, providing more efficient and data-driven solutions. As we look to the future, the synergy between SEO and AI is likely to shape the next frontier of online visibility and user experience. Ultimately, the overarching goal of SEO, now complemented by AI, remains centred on delivering valuable content and a seamless user experience, harmonising the needs of both website visitors and search engines.

